Figure 7.
GMP-compatible conditions: Stability and freezing
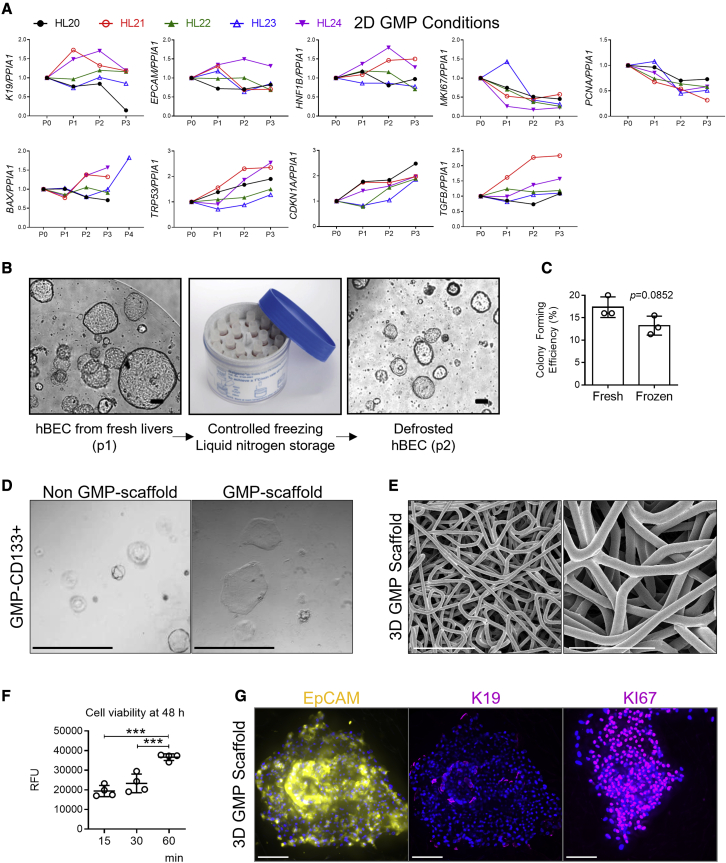
(A) Gene expression of genes associated with mature cholangiocytes (K19, EpCAM, HNF1B), proliferation (MKI67, PCNA), induced apoptotic cell death (BAX), and cellular senescence (TRP53, CDKN1A, and TGFB) normalized to PPIA1 for hBECs isolated from 5 human donor livers (HL20 to HL24) over the course of three passages in 2D GMP-compliant scaffolds. Data normalized to freshly isolated hBECs.
(B) CD133+ cells isolated from fresh livers (here depicted at passage 1) can be stored long term in liquid nitrogen and later cultured again (here depicted at passage 2) as organoids in non-GMP-compliant conditions (n = 4 biological replicas). Scale bar, 100 μm.
(C) Colony-forming efficiency of fresh and frozen hBECs show no significant differences. Student’s t test (n = 3).
(D) CD133+ hBECs isolated in GMP-compliant conditions can be cultured as organoids in non-GMP conditions in Matrigel spheres (left). They can be cultured as well in two-dimensional GMP-compliant conditions (right). Both images represent passage 2 after isolation from fresh livers (n = 4 biological replicas). Scale bar, 60 μm.
(E) Polycaprolactone scaffolds electron microscopy. Scale bars, 100 μm (left), 50 μm (right).
(F) hBECs isolated in GMP-compliant condition viability after 48 h culture in polycaprolactone scaffolds. y axis indicates time allowed for hBEC seeding in the scaffolds. y axis indicates RFU (relative fluorescence units). ∗∗∗ denotes p < 0.001 (mean ± SEM), one-way ANOVA (n = 4).
(G) hBECs isolated in GMP-compliant conditions and cultured for 1 week in polycaprolactone scaffolds retain cholangiocellular markers (EpCAM and K19) and show signs of proliferation as seen by KI67 immunofluorescence (n = 3 biological replicas). Scale bars, 100 μm.