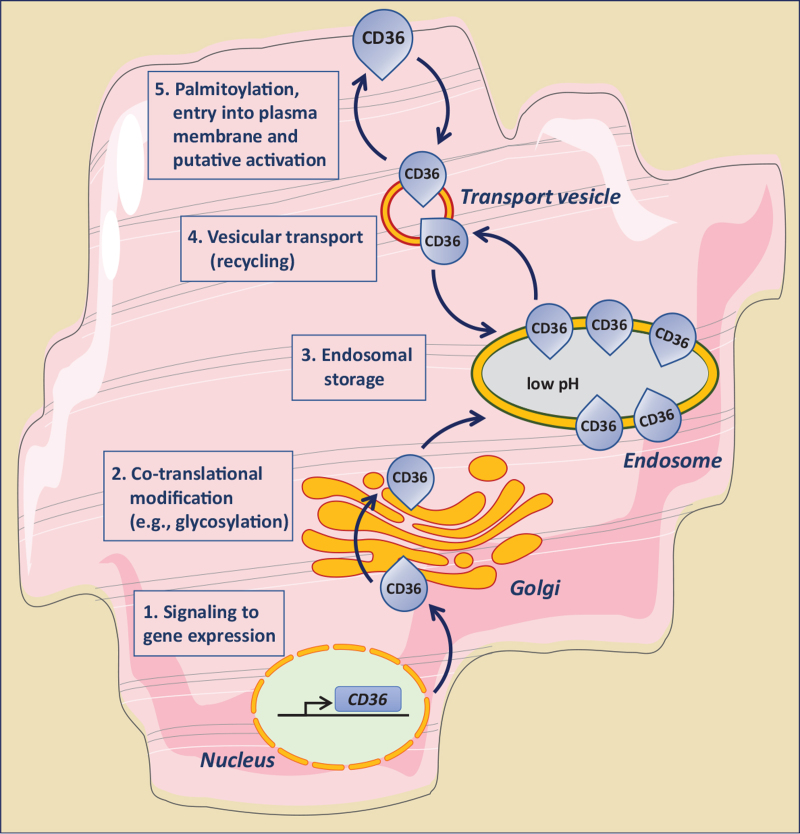
FIGURE 3.
Schematic presentation of the five distinct levels at which the functioning of CD36 in cellular fatty acid uptake can be modulated. 1. Intervention of signaling pathways affecting CD36 gene expression. 2. Intervention in co-translational modification of CD36, in particular its glycosylation. 3. Manipulation of the endosomal storage of CD36. 4. Modulation of the reversible vesicular transport of CD36 between an endosomal storage compartment and the plasma membrane (subcellular recycling). 5. Influencing CD36 palmitoylation, its insertion into the membrane bilayer, and putative activation (e.g., interaction with other membrane-associated proteins). CD36, cluster of differentiation 36.