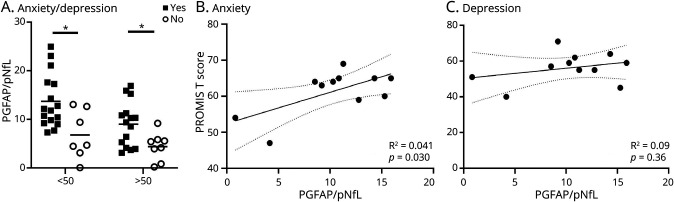
Figure 4. Higher Neuroglial Score Correlates With Anxiety in Neuro-PASC Patients.
Neuro-PASC patients (posthospitalization neuro-PASC patients and nonhospitalized neuro-PASC patients combined) presenting with anxiety and/or depression (A) in the Neuro–Covid-19 clinic showed higher neuroglial scores when compared with neuro-PASC patients who exhibited neither anxiety nor depression in both younger than 50-year age-group and older than50-year age-group (younger than 50 years: yes, n = 17; no, n = 7, p = 0.01, Hedges' g effect size = 1.37; older than 50 years: yes, n = 15; no n = 8, p = 0.02, Hedges' g effect size = 1.17; two-tailed T tests). Quantitative PROMIS-57 T scores for anxiety (B) but not depression (C) showed linear correlation with increasing glial activation predominance at the time of sample (anxiety T score: n = 11, R2 = 0.41, p = 0.03; depression T score: n = 11, R2 = 0.09, p = 0.36; two-tailed Pearson correlation). *p ≤ 0.05.