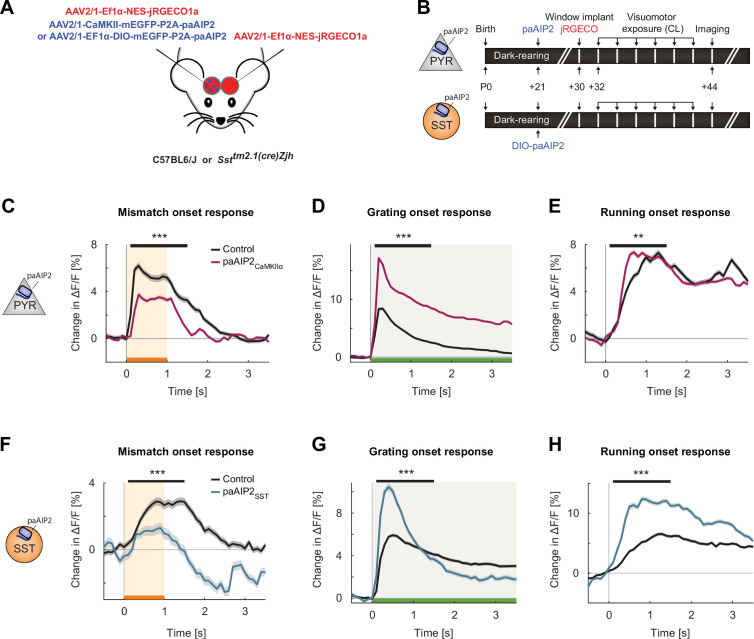
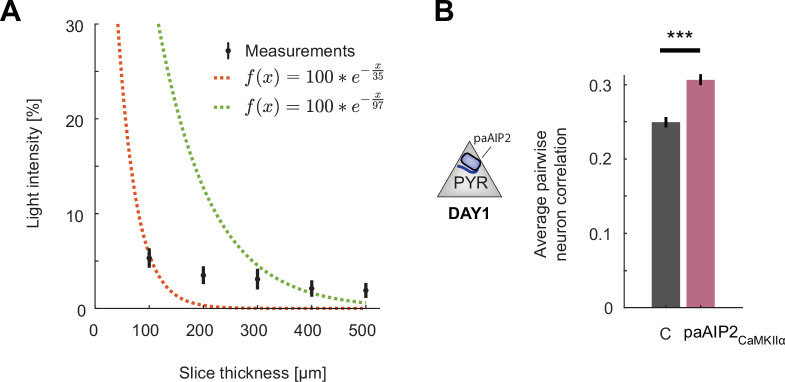
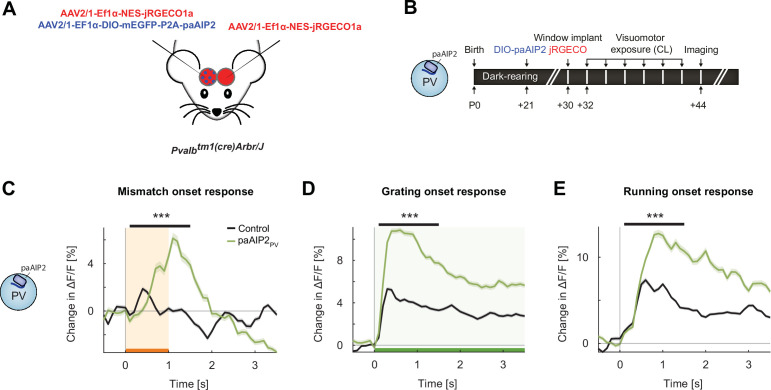
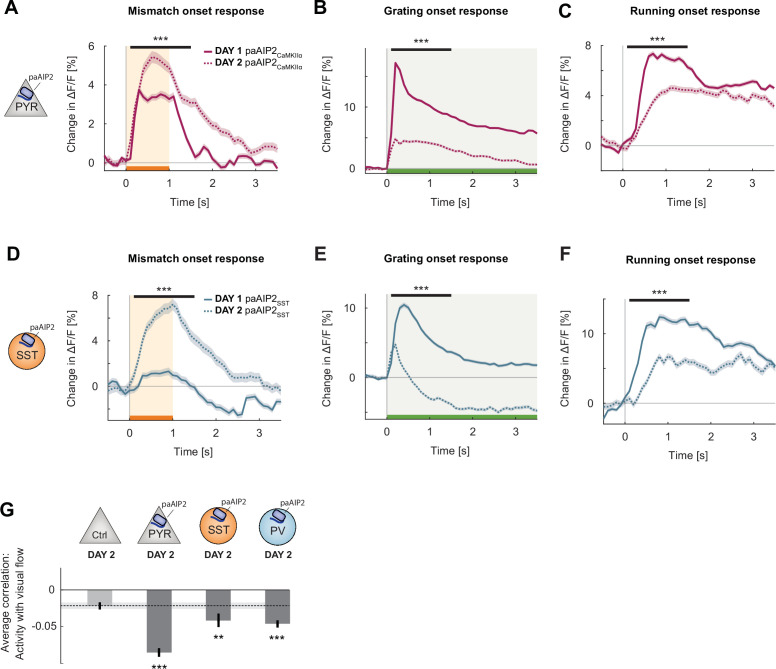
Figure 6. Inhibiting calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinase II (CaMKII) in excitatory neurons or somatostatin (SST) interneurons resulted in imbalanced visuomotor responses in L2/3 excitatory neurons.
(A) We injected an AAV2/1-CaMKII-mEGFP-P2A-paAIP2 (in C57BL/6J mice) or AAV2/1-Ef1α-mEGFP-P2A-paAIP2 (in SST-Cre mice) unilaterally in V1 to express the photoactivatable CaMKII inhibitor paAIP2 in excitatory or SST interneurons, respectively, and an AAV2/1-Ef1α-NES-jRGECO1a bilaterally to express the calcium indicator jRGECO for imaging in L2/3 excitatory neurons. (B) Mice were dark-reared from birth. Adeno-associated viral vector (AAV) injections occurred at postnatal day 21 (paAIP2 or DIO-paAIP2) and P30 (jRGECO1a). Imaging window implantation occurred on P30. Mice had six sessions of visuomotor exposure in a closed-loop (CL) virtual environment during which we illuminated cortex bilaterally with blue light (473 nm) to inhibit CaMKII. We used six C57BL/6J mice, in which paAIP2 was targeted to excitatory neurons using a CaMKIIα(1.3 kb) promoter (paAIP2CaMKIIα), and seven SST-Cre mice that received an injection of the DIO-paAIP2 vector (paAIP2SST). (C) The average L2/3 population response to mismatch was stronger in control (black) than in paAIP2CaMKIIα (purple) hemispheres. Shading indicates the standard error of the mean (SEM) across neurons. Orange shading and bar indicate the duration of mismatch. Mean responses were compared across neurons in the time window marked by the black bar above the traces. Here and in subsequent panels, n.s.: p>0.05, *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. For all details of statistical testing, see Supplementary file 1A. (D) As in (C), but for responses to the onset of a drifting grating stimulus (see Materials and methods). Green shading and bar indicate the presence of grating stimulus. (E) As in (C), but for running onset responses in the CL condition. (F) As in (C), but for inhibition of CaMKII in SST interneurons. (G) As in (D), but for inhibition of CaMKII in SST interneurons. (H) As in (E), but for inhibition of CaMKII in SST interneurons.