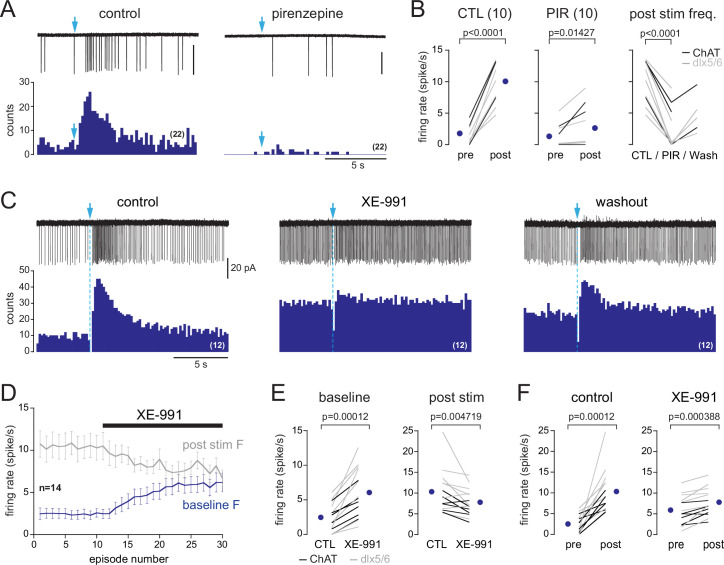
Figure 6. M1 muscarinic ACh receptors (mAChRs) mediate basal forebrain (BF)-evoked excitation by closing M channels.
(A) Photo-evoked loose cell-attached (LCA) responses and cumulative peri stimulus time histograms (PSTHs) (over 22 consecutive sweeps, 200 ms/bin) recorded in a periglomerular (PG) cell from a dlx5/6 mouse in control condition (left) and in the presence of the M1 mAChR antagonist pirenzepine (2 µM). Scale bar for traces 50 pA. (B) Summary graphs. Firing rate before (pre) and after (post) photostimulation of BF fibers in control condition (left, paired t-test) and in the presence of pirenzepine (PIR, 1 or 2 µM, paired Wilcoxon signed-rank-sum test). Right graph shows that pirenzepine decreased BF-evoked excitation in every cell tested (paired t-test). Partial washout was obtained in five cells. Cells were recorded in choline acetyltransferase (ChAT) mice (n = 3, black lines) and dlx5/6 mice (n = 7, gray lines). (C) Photo-evoked LCA responses and cumulative PSTHs recorded in a PG cell from a dlx5/6 mouse showing the effects of the M-channel blocker XE-991 (10 µM) on spiking frequency. BF fibers were photostimulated with a single flash (blue arrow and dotted line). (D) XE-991 increased baseline spiking rate (blue line, measured during a 15 s time period preceding the flash) and decreased post-stimulus spike frequency (gray line). Average from 14 cells (eight in dlx5/6 mice, six in ChAT mice). Each episode was 30 s long. (E) Summary graph showing the two effects of XE-991 on each cell. Paired Wilcoxon signed-rank-sum tests. (F) Firing rate before (pre) and after (post) photostimulation of BF fibers in control condition (left, paired Wilcoxon signed-rank-sum test) and in the presence of XE-991 (t-test). Experiments were all done in the presence of 6-nitro-7-sulfamoylbenzo[f]quinoxaline-2,3-dione (NBQX) (10 µM), D-2-amino-5-phosphonopentanoic acid (D-AP5) (50 µM), and mecamylamine (50 µM). Means are the blue circles.