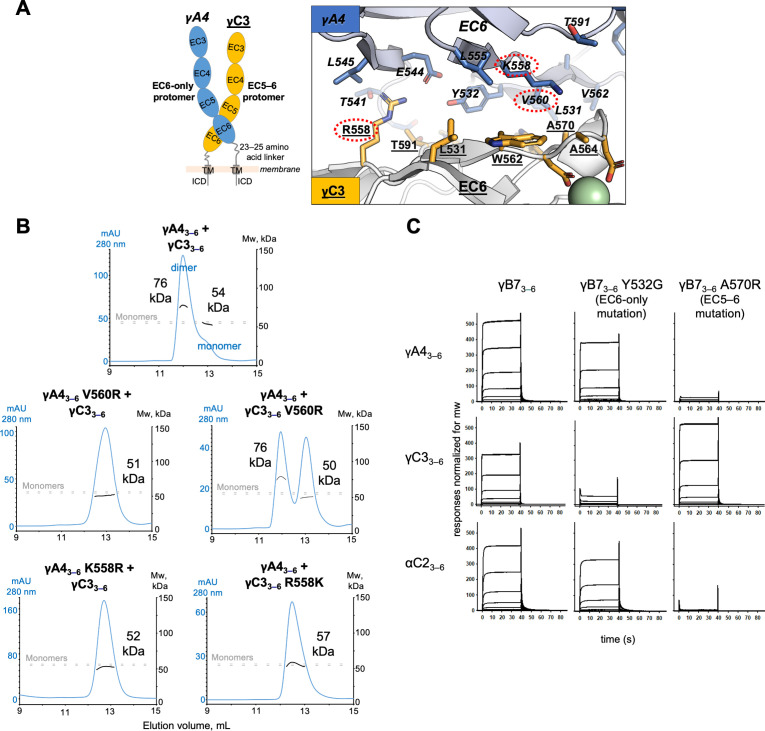
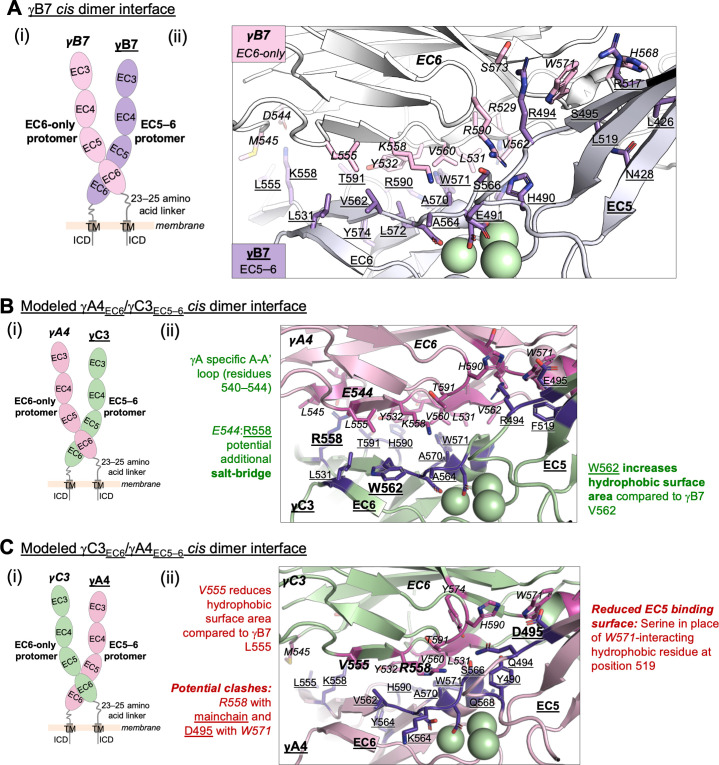
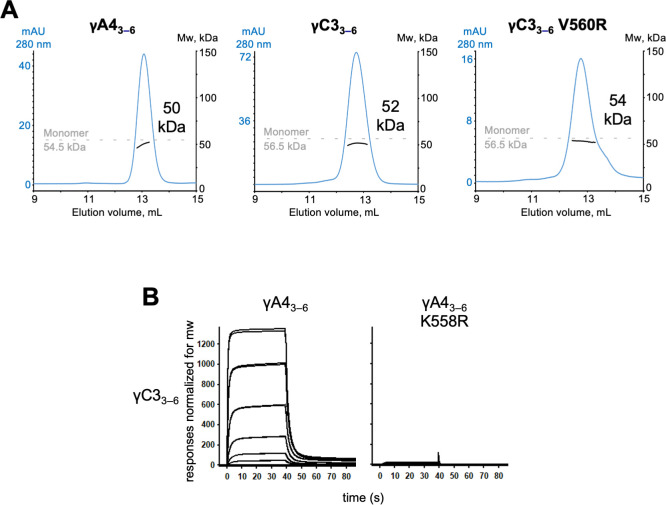
Figure 5. γA4 preferentially forms the EC6-only side and γC3 the EC5–6 side in cis dimers.
(A) Structural model of γA4/γC3 cis dimer based on γB7EC3–6 cis dimer and γA4EC3–6 crystal structures (PDBs: 5V5X and 5SZQ). γA4 is shown adopting the EC6-only side (blue protomer) and γC3 is shown adopting the EC5–6 side (yellow protomer). Left, schematic of the γA4/γC3 EC3–6 cis dimer. Right, close-up view of the EC6:EC6 interface from the modeled cis dimer showing interfacial residue side chains. Bound calcium ions are shown as green spheres. Residues which were mutated in the panel B are circled in red. γB7 crystal structure numbering is used for both γA4 and γC3 residues. See methods for γA4 and γC3 alignment. Please note the model shown here is solely for hypothesis generation, since it is unlikely to be completely accurate. See methods for further details of structural modeling. (B) Top, size exclusion-coupled multiangle light scattering (SEC-MALS) data for an equimolar mixture of wild-type γA4EC3–6 and γC3EC3–6 showing dimer formation. Plot shows size exclusion absorbance at 280 nm trace (left axis), molecular weight of the eluant peaks (right axis), and the monomer molecular weights of γA4EC3–6 and γC3EC3–6 measured by mass spectrometry – 54.5 and 56.5 kDa, respectively – as dashed gray lines. Average molecular weight of the molecules in the dimer and monomer eluant peaks are labeled. Middle, SEC-MALS data for V560R mutants, which target the EC6-only side of the interface. Bottom, SEC-MALS data for residue 558 mutants. The γC3-like K558R mutation in γA4 inhibits heterodimer formation with wild-type γC3. Similarly, the γA4-like R558K in γC3 inhibits dimerization with wild-type γA4. (C) SPR-binding profiles for γB7EC3–6 wild-type and cis interface mutants flowed over three individual wild-type cis fragment surfaces. The two mutations specifically target one side of the cis interface.