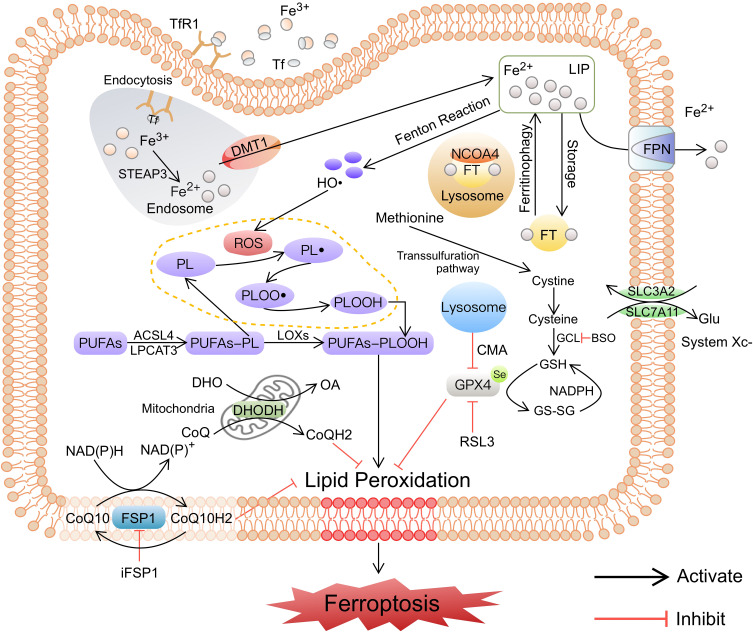
Figure 1.
The major induced pathways of ferroptosis. The induced pathways of ferroptosis, including iron metabolism disorder, lipid peroxidation, and failure of antioxidant systems, are summarized. Iron metabolism and lipid metabolism disorders lead to LPO accumulation, the failure of antioxidant systems leads to LPO not being removed in time, and the above process ultimately induces ferroptosis.
Abbreviations: Tf, transferrin; TfR1, transferrin receptor 1; Fe2+, ferrous iron; Fe3+, ferric iron; LIP, labile iron pool; FPN, ferroportin; FT, ferritin; NCOA4, nuclear receptor coactivator 4; HO•, hydroxyl radicals; ROS, reactive oxygen species; LOXs, lipoxygenases; PL, phospholipid; PL•, phospholipid radical; PLOO•, phospholipid peroxyl radical; PLOOH, phospholipid hydroperoxide; PUFA, polyunsaturated fatty acid; GPX4, glutathione peroxidase 4; GSH, glutathione; GS-SG, oxidized glutathione; GCL, glutamate-cysteine ligase; Glu, glutamic acid; CMA, chaperone-mediated autophagy; FSP1, ferroptosis suppressor protein 1; CoQ10, coenzyme Q10; DHODH, dihydroorotate dehydrogenase; DHO, dihydroorotate; OA, orotate; iFSP1, inhibitor of ferroptosis suppressor protein 1.