FIG 1. Characteristics of various inflammasomes.
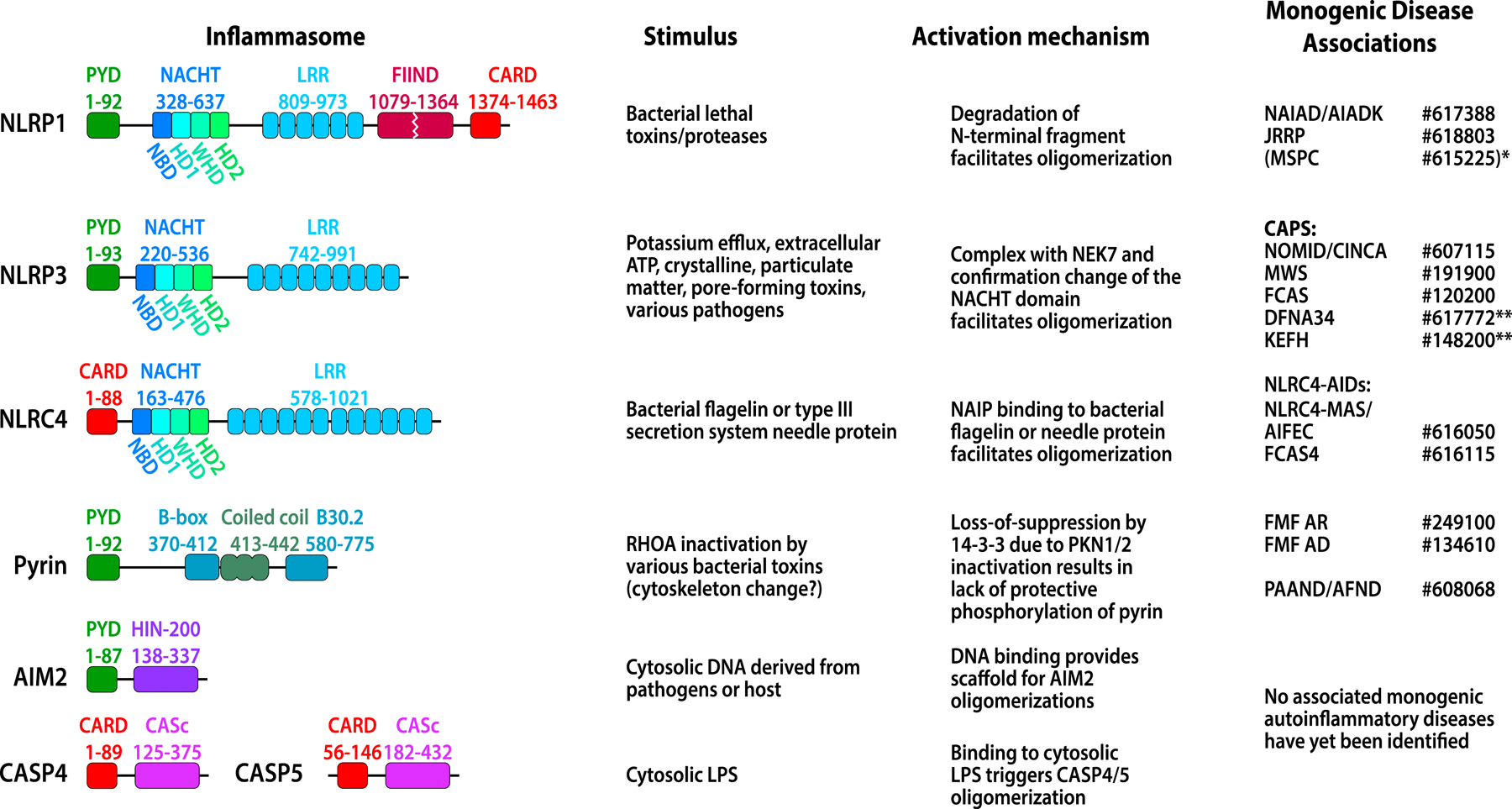
CARD domain or PYD domain is responsible for recruiting ASC and for forming ASC specks. Other domains function as regulatory domains to prevent inflammasome autoactivation (detailed in Fig 2). Diseases related to the inflammasomes are shown in the last column with the MIM numbers (www.oimm.org). Diseases in bracket typically do not present with systemic inflammation. See text for full name of the diseases. NLRP1-associated: NAIAD or AIADK; JRRP. *MSPC is caused by mutations in the pyrin domain of NLRP1 and leads to a precancerous skin condition without systemic inflammation. NLRP3-associated: The disease spectrum of CAPS includes the 3 severity phenotypes: NOMID, MWS, and FCAS. ** DFNA34, (Deafness, autosomal dominant 34) and **KEFH, (Keratoendothelitis fugax hereditaria) present with inflammation restricted to the inner ear and the cornea respectively with absent or minimal systemic inflammation. NLRC4-associated AIDs include NLRC4-MAS/AIFEC presenting with recurrent MAS and FCAS4 presenting with more systemic inflammation and rash. MEFV/pyrin-associated AIDs include additive gain-of function, AR (autosomal recessive) and AD (autosomal dominant) FMF, and PAAND/AFND caused by mutations in two 14–3-3-binding serine residues. Mutations in AIM2 and CASP4 have so far not been associated with human monogenic diseases.
