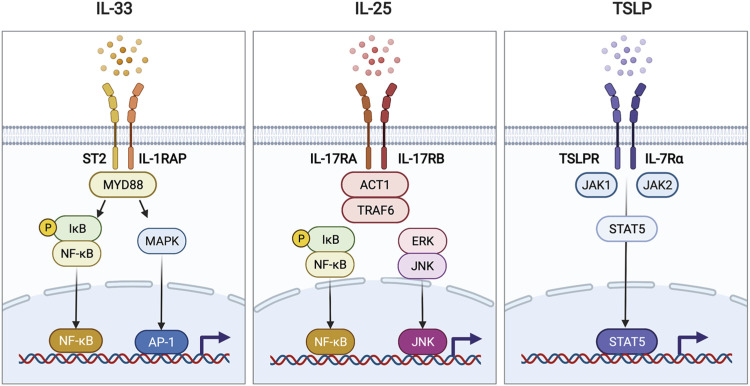
Figure 2. The receptors and downstream signaling of each alarmin. IL-33 binds to a heterodimeric receptor composed of ST2 and IL-1RAP. Ligation of IL-33 recruits and activates the adaptor protein MyD88. MyD88 activates the transcription factors NF-κB and AP-1, which are then delivered to the nucleus and bind to specific DNA motifs. IL-25 exerts its pro-inflammatory effects by binding to a heterodimeric receptor composed of IL-17RA and IL-17RB. The intracellular domain of the IL-25 receptor recruits ACT1 and TRAF6 and subsequently promotes the activation of the NF-κB or ERK-JNK signaling axis. TSLP binds to TSLPR paired with IL-7Rα. This ligation event activates TSLP receptor-associated JAK1 and JAK2, which activate the transcription factor STAT5, thereby causing it to translocate into the nucleus. All of these alarmin signaling pathways lead to the production of type-2 cytokines and chemokines by the target cells.
IL-1RAP, IL-1 receptor accessory protein.