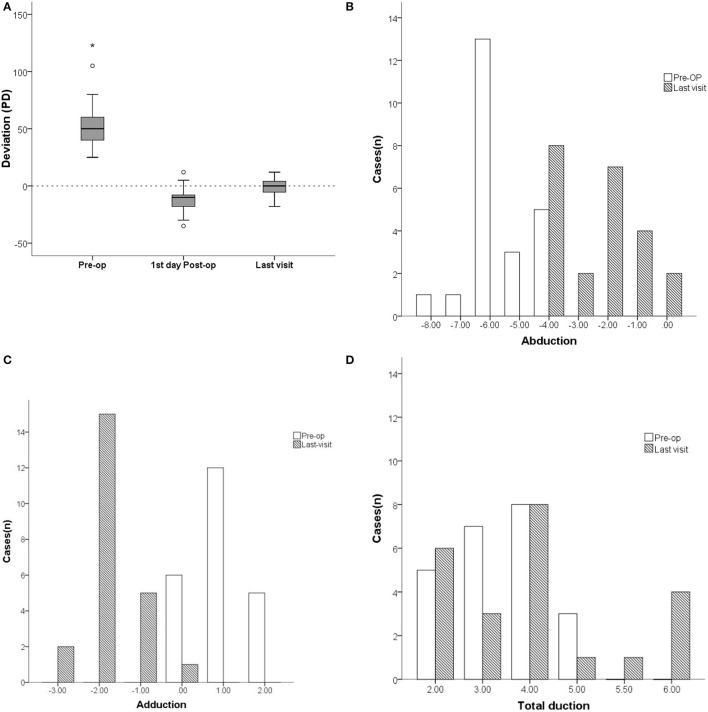
Figure 1.
Comparison of deviation (PD) and ocular motility between pre- and postoperation of patients with unilateral complete abducens nerve plasy. (A) The mean pre-operative horizontal esodeviation of 55.5 ± 27.2 PD (range: +25 to +123) significantly improved to −11.5 ± 11.0 PD (range: −35 to +12) on the first day after surgery, and further improved to 0.04 ± 7.3 PD (range: −18 to +12) as determined on their last visit. (B) The mean abduction function increased form −5.6 ± 1.0 (range: −8 to −4) preoperatively to −2.4 ± 1.4 (range: −4 to 0) on their last visit. (C) The mean adductions of the paretic eye decreased from 0.0 ± 0.0 (range: 0 to +2) pre-operatively to a mean deficiency of −1.8 ± 0.7 (range: −3 to 0) on their last visit. (D) The mean duction ranges in the paretic eye increased from 2.4 ± 1.0 pre-operatively to 3.8 ± 1.4 on their last visit. In the box plot (A), the value that is more than 1.5 times the distance from the quartile value is the outlier and is represented by “o”, while the value that is more than 2 times is the extreme value and is marked by “*”. Pre-op, pre-operatively.