Figure 3.
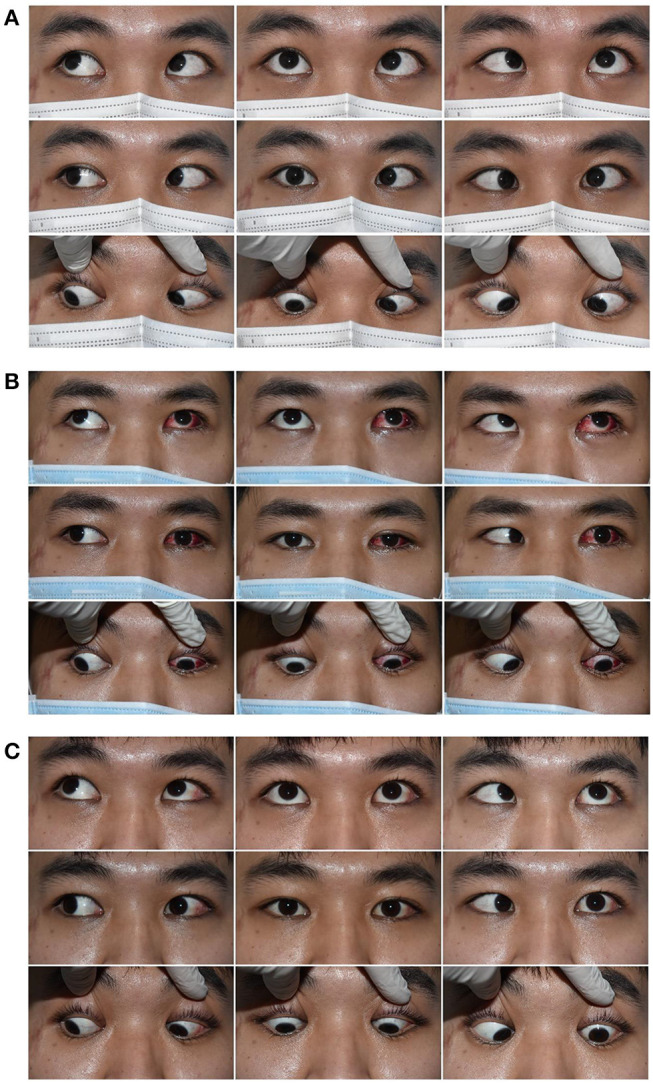
Typical case 1 showed the patient with abduction = −4 on the last visit. A 24-year-old male whose left eye deviated inward for 10 months after an injury resulting from a fall. He was diagnosed as a complete traumatic abducens nerve palsy and received a medial rectus recession of 10 mm and lateral rectus resection of 13 mm in his left eye while under general anesthesia. The FDT performed during surgery was negative. (A) The patient's 9-gaze eye position photo is shown preoperatively with left eye esotropia 50PD (LET = 50PD), abduction-6, adduction +1. (B) 1 day postoperatively with left eye exotropia 30PD (LXT = 30PD), abduction-2, adduction-4. (C) 2 months postoperatively with esotropia 3PD (ET = 3PD), abduction-4, adduction-2.
