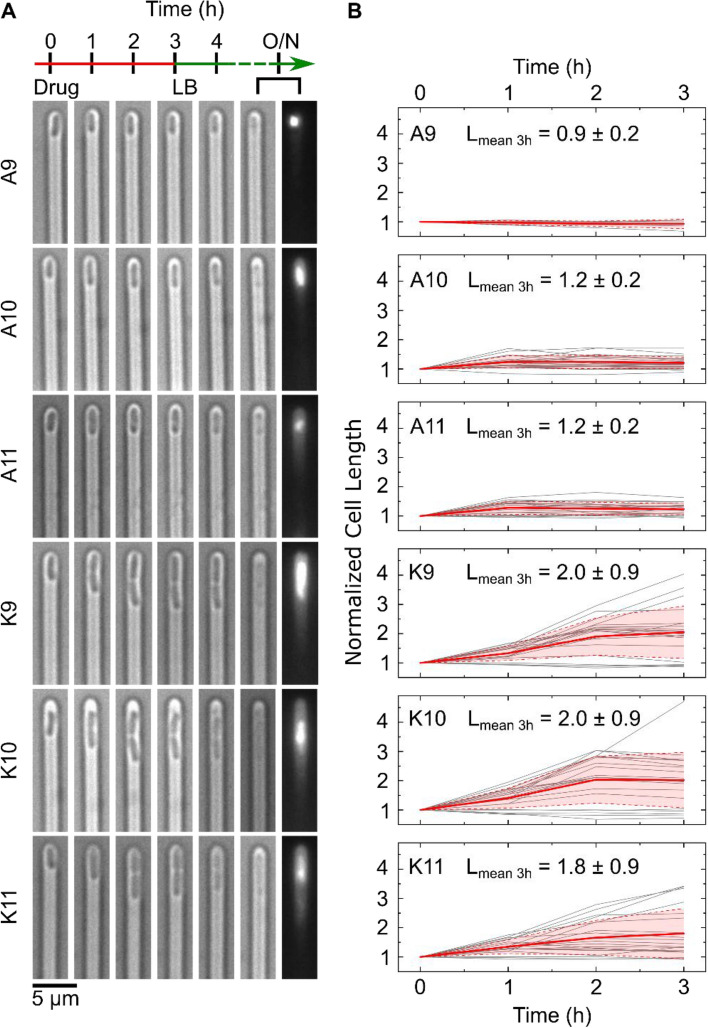
Figure 3.
Comparing the single-cell killing phenotypes of our two experimental peptide series. The single-cell microscopy images in (A) depict differences in the killing phenotypes between the bienA and bienK peptides. The first image in each set (at t = 0) refers to the point at which drug dosage starts, with the next images showing the cell at hourly intervals over 3 h of drug treatment (all peptides were dosed at 10 µM concentrations). The following image shows the cell after 1 h of LB incubation, followed by images showing the debris of the dead cell after overnight (O/N) incubation in LB (bright-field and corresponding PI stain fluorescence image). The bienA series kill the cells rapidly, with the cells showing minimal elongation before growth arrest and death. This is also apparent from the corresponding graphs, shown in (B), tracking the lengths of individual cells (lengths are normalized to the initial cell length). Individual cell traces are provided in grey, with the mean (red) and standard deviation (red shaded area) depicted. The cellular length changes (before death) and distributions are relatively homogeneous for the bienA peptides. In stark contrast, the bienK peptides showed much greater heterogeneity in the lengths. Interestingly, for all three bienK peptides, we observed cells dying during septation. However, as mentioned previously and as seen in the plots in (B), this was not the only phenotype. On average, with the bienK peptides, cells doubled in length before growth arrest and death, but there was significant spread in the lengths, as shown in the mean lengths (normalized) at the 3 h time-point reported inset in each plot (mean ± std. dev.). Note, for this analysis, we studied a subset of cells that were susceptible to the peptides, and were killed before undergoing any cell division. We chose a subset of 20 cells from 2 independent biological repeats for all the peptides, with the exception of bienA9 (5 cells, 1 experiment) which had far fewer cells showing the necessary characteristics. To reiterate, these subsets of cells were chosen according to the following criteria—(i) the cells were susceptible to the drug, (ii) they died before dividing and (iii) they did not disintegrate immediately after treatment, since we wished to track their length over the entire course of drug treatment (3 h).