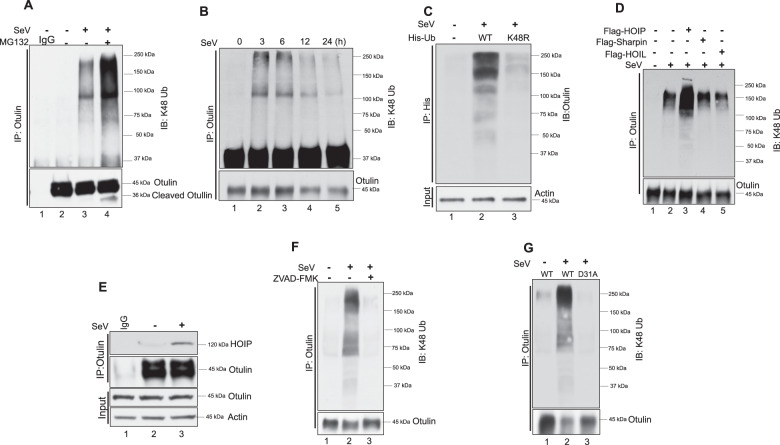
Fig. 5. Otulin is K48 ubiquitinated.
A Otulin K48 ubiquitination was analyzed in HT1080 cells after SeV infection (MOI 10) for 24 h followed by immunoprecipitation with Otulin antibody and immunoblotting with K-48 ubiquitin antibody. MG132 was added for 4 h before harvesting cells. B Otulin K48-ubiquitination was analyzed post-SeV infection for the indicated time points. Immunoprecipitation was performed with Otulin antibody and immunoblotting was done with K-48 ubiquitin antibody. C To show Otulin K48 ubiquitination after transfection of His-Ub WT and His-UbK48R in HT1080 cells overnight followed by SeV infection for 24 h. Cells were lysed in denaturing lysis buffer (6 M guanidine-HCl, 0.1 M Na2HPO4/NaH2PO4, 10 mM imidazole; pH 8.0), sonicated, and centrifuged. His-Ub was pulled down with Ni-NTA resin and immunoblot analysis was done with Otulin antibody. D Otulin K48 ubiquitination was assessed in cells transfected with Flag-tagged HOIP, HOIL or Sharpin. HOIP/HOIL/Sharpin were transfected overnight followed by SeV infection for 24 h. E Immunoprecipitation assay to show an interaction of HOIP with Otulin post-SeV infection for 1 h. F Otulin K48 ubiquitination was analyzed in the presence or absence of Z-VAD-FMK post-SeV infection. Immunoprecipitation assay was performed with Otulin antibody and immunoblot analysis was done with K48-Ub antibody. G OT-KD cells reconstituted with Otulin WT and Otulin D31A were assessed for Otulin K48 ubiquitination post-SeV infection. Immunoprecipitation assay was performed with Otulin antibody and immunoblot analysis was done with K48-Ub antibody. Quantification of western blots and statistical analyses are provided in Supplementary Fig. 8 (mean ± SEM, n = 3; ns > 0.05; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001).