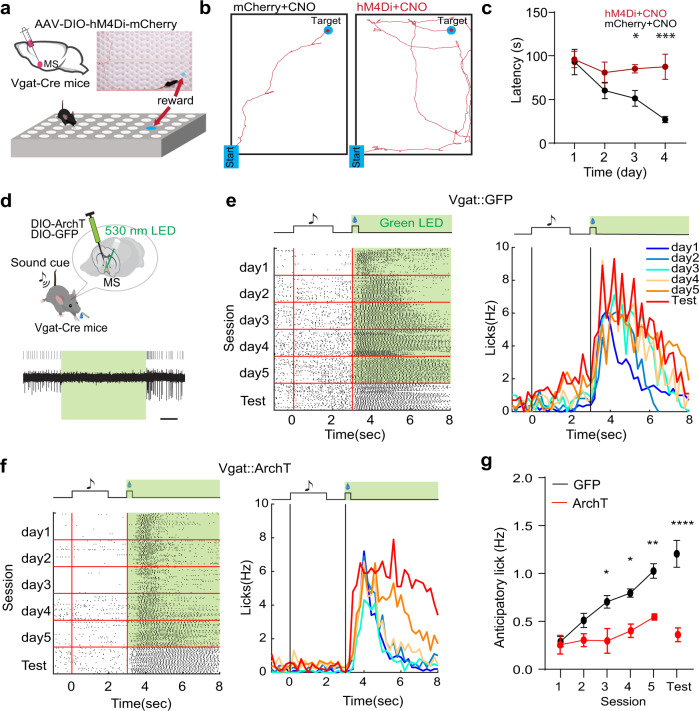
Fig. 4. MS GABAergic neurons are required for reward associative learning.
a Hole-board test while chemogenetically silencing MS GABAergic neurons. Top inset, photograph with superimposed movement track of an example animal locating the reward. b Movement tracks for an example mCherry control animal injected with CNO (left) and a hM4Di-expressing animal injected with CNO (right) tested on day 4. c Average latencies for reward localization over training days. Day1, p = 0.8586, D2, p = 0.1863, D3, *p = 0.0264, D4, ***p = 0.0008, two-way ANOVA, post-hoc Fisher’s LSD test, two-sided, n = 3 mice in each group. Error bars indicate s.e.m. d Cue-reward associative learning while optogenetically silencing MS GABAergic neurons. Bottom, slice recording from an ArchT-expressing MS neuron showing suppression of neuronal spikes by green light (530 nm). Scale, 1 s. e Raster plot of licking events (left) or peri-event lick rate (right) during training sessions (over 5 days) and in the test session (on day 6) for an example GFP control mouse. Green LED light was applied during the US delivery window (5 s) throughout trials. Licks between onsets of CS (sound cue) and US (sucrose) are defined as anticipatory licks. f Similar to (e), but for an ArchT-expressing mouse. g Average anticipatory lick rates across training sessions and in the test session for GFP control (n = 4) and ArchT (n = 3) groups. D1, p > 0.9999, D2, p = 0.6017, D3, *p = 0.0132, D4, *p = 0.0188, D5, **p = 0.0032, Test, ****p < 0.0001, two-way ANOVA, post-hoc Bonferroni test, two-sided. Error bars indicate s.e.m. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.