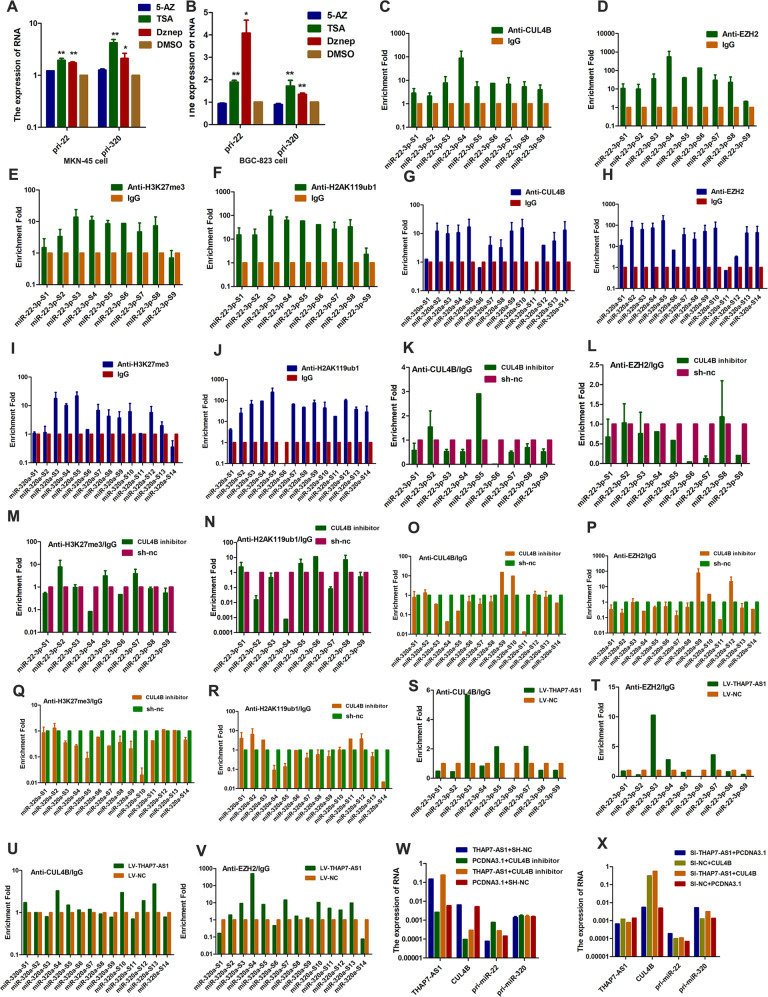
Fig. 7. THAP7-AS1-CUL4B complex transcriptionally represses the expression of miR-22-3p/miR-320a by CUL4B-catalyzed H2AK119ub1 and EZH2-mediated H3K27me3.
A–B MKN-45 (A) and BGC-823 (B) cells were treated with 5-Azacytidine (5-AZ), Trichostatin A (TSA) and deazaneplanocinA (Dznep). C–F We used primers that were located ~1 kb upstream and downstream of the TSS of miR-22-3p (sites S1–S9) of CUL4B-binding sites. ChIP assays with an anti-CUL4B (C), anti-EZH2 (D), anti-H3K27me3 (E) and anti-H2AK119ub1 (F) or negative control (anti-IgG) antibodies showed these four proteins could bind to the miR-22-3p promoter in MKN45 cells. G–J We used primers that were located ~1 kb upstream and downstream of the TSS of miR-320a (sites S1–S14) of CUL4B-binding sites. ChIP assays with an anti-CUL4B (G), anti-EZH2 (H), anti-H3K27me3 (I), and anti-H2AK119ub1 (J) or negative control (anti-IgG) antibodies demonstrated these four proteins could bind to the miR-320a promoter in MKN45 cells. K–N ChIP assays of miR-22-3p promoter primers in CUL4B knockdown MKN-45 cell using indicated antibodies. O–R ChIP assays of miR-320 promoter primers in CUL4B knockdown MKN-45 cell using indicated antibodies. S–V ChIP assays of miR-22-3p (S–T) or miR-320 (U–V) promoter primers in LV-THAP7-AS1 MKN-45 cells using indicated antibodies. W–X RT-qPCR assay was performed to detect primary miR-22-3p and miR-320a in MKN-45 cells transiently transfected with indicated RNA and plasmid. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.