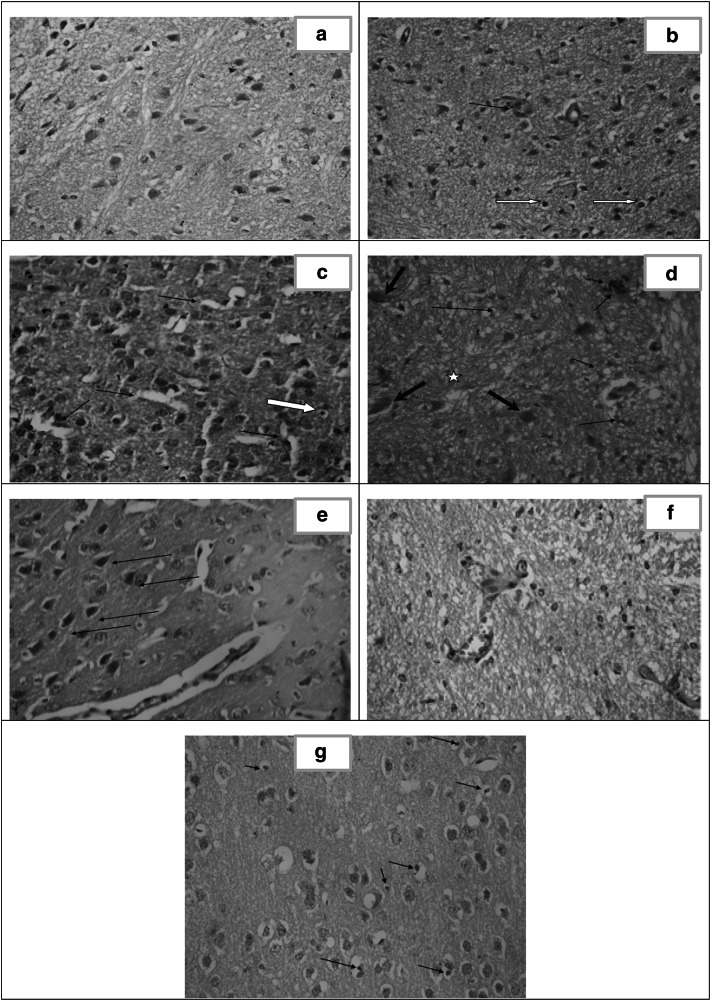
Fig. 6.
Histopathological study of the brain. a Section in brain of healthy control (group I) showing normal cortex architecture. [H&E X400]. b Section of cerebral cortex of infected untreated control (group II) showing gliosis, apoptosis [white arrows] and perivascular inflammatory infiltrate [arrow]. [H&E X400]. c Brain section of CS NPs treated group (III) showing astrocyte proliferation [gliosis], apoptosis [white arrow] and dilated sinuses [arrows]. [H&E X40]. d Brain section of spiramycin treated group (IV) showing gliotic nodule [star], dead neurons [red arrows] together with perivascular and parenchymal inflammatory infiltrate [black arrows]. [H&E X400]. e Brain section of spiramycin-metronidazole treated group (V) showing mild congested blood vessels, moderate gliosis and mineralized bodies of necrotic neurons so called ferrugination [arrows]. [H&E X400]. f Brain section of spiramycin-CS NPs 400 mg/kg treated group (VI) showing mild dilation of blood vessels (BV) with absence of tachyzoites and near normal architecture. [H&E X 400]. g Brain section of spiramycin-CS NPs 100 mg/kg treated group (VII) showing moderate gliosis, dispersed apoptotic cells [arrows] and extensive vacuolation in the cortex [spongiosis]. [H&E X 400]