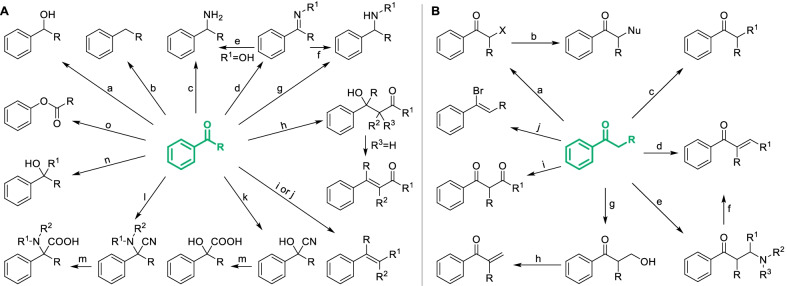
Scheme 12.
Classical derivatization strategies of phenylketone fragments. A Derivatization of carbonyl. Common conditions: a NaBH4/alcohol b Zn-Hg/HCl (Wolff-Kishner reduction) or NH2NH2/base/ high temperature (Clemmensen reduction) or HS(CH2)3SH/BF3·Et2O or NaBH4/TFA (Gribble reduction for R = aryl) c NH4OAc/NaBH3CN/alcohol d R1NH2 e Pd/H2 or Zn/H+ f NaBH4/alcohol g R1NH2/NaBH4/Lewis acid h R1COCH R2R3 i CH2R1R2 (R1,R2 = elctron withdrawing group) j Ph3P = CR1R2 (Wittig reaction) or (OEt)2POCHR1R2 (Wittig–Horner reaction) k TMSCN/Lewis acid l NHR1R2/(EtO)2POCN m H2O n R1MgBr or R1Li o peroxy acid; B Derivatization of acetophenone fragments. Common conditions: a halogenating reagents b nucleophile c R1X, base d R1CHO, base e R1CHO, NHR2R3 f CH3I/base/Δ g HCHO, base h oxalic acid i RCOOEt, base j PBr3