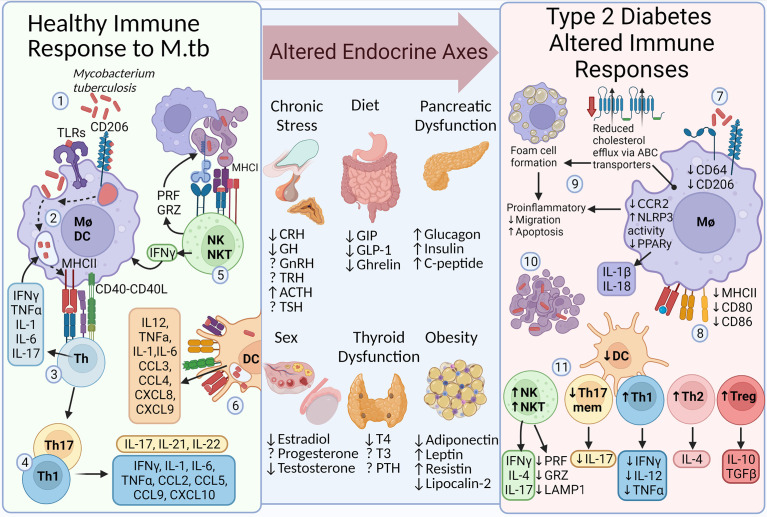
Figure 2.
Altered endocrine signaling affects the appropriate immune response to infection. In an otherwise healthy immune system, the response to Mycobacterium tuberculosis includes several essential functions. 1, PAMP-PRR interaction (e.g. TLR4 and CD206) and phagocytosis. 2, Phagosome-lysosome fusion and presentation (MHCII). 3, Activation of adaptive immune responses (CD40-CD40L) enhances the innate killing response via cytokines (e.g. IFNγ). 4, Th1 and Th17 predominate, stimulating mycobacterial control and immune cell influx via cytokine and chemokine release. 5, NK cells induce apoptosis, allowing efferocytosis by macrophages, and enhance killing by IFNγ release. 6, DCs also promote killing, antigen presentation, and immune cell chemotaxis. The immune response is influenced by sex hormone production, diet-induced gastric hormones, stress-related responses from the brain stem, thyroid dysfunction, and the development of chronic metabolic diseases such as T2D and obesity. Thus, the immune response to M. tuberculosis is altered during T2D. 7, Macrophage PRR expression (e.g. CD64 and CD206), phagocytosis, and killing is diminished. 8, Expression of antigen presenting proteins is reduced. 9, Expression of cholesterol efflux transporters (ABC) is reduced, leading to cholesterol accumulation and foam cell formation. Foam cells have reduced migratory capacity and increased rate of apoptosis. 10, Reduced efferocytosis results in a cholesterol rich environment and providing a niche for mycobacterial growth. 11, Additionally, altered ratios of Th cell subsets and dendritic cells influence cytokine levels. PAMP, pathogen-associated molecular pattern; PRR, pattern recognition receptor; TLR, toll-like receptor; MHC, major histocompatibility complex; Mφ, macrophage; DC, Dendritic cell; Th, CD4+ helper T cell; PRF, perforin; GRZ, granzyme; Treg, regulatory T cell; ABC, ATP-binding cassette cholesterol transporter; T2D, Type 2 Diabetes; TB, Tuberculosis; CRH, corticotropin-releasing hormone; GH, growth hormone; GnRH, gonadotropin-releasing hormone; TRH, thyrotropin -releasing hormone; ACTH, adrenocorticotropic hormone; T4, Thyroxine; T3, triiodothyronine; TSH, thyroid-stimulating hormone; PTH, parathyroid hormone; GIP, gastric insulinotropic peptide; GLP-1, glucagon-like peptide 1; TSH, thyroid-stimulating hormone; DHEA, dehydroepiandrosterone; This figure was created with BioRender.com.