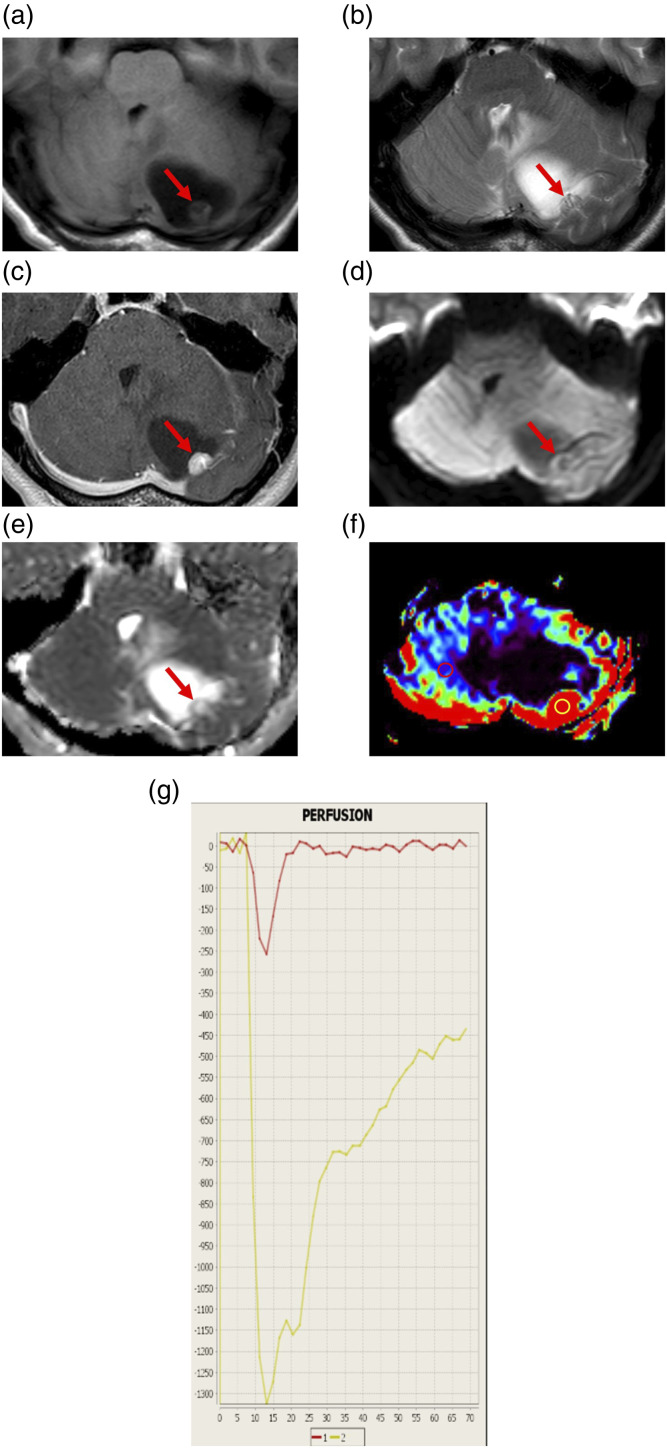
Figure 1.
Representative magnetic resonance imaging findings of a 35-year-old woman with hemangioblastoma (Case 1). (a) Axial T1-weighted image (T1WI) showing a cystic mass lesion with a mural nodule in the left cerebellar hemisphere. The cystic lesion is low-intense, while the nodule (arrow) is slightly low-intense compared to the cerebellum. (b) Axial T2WI showing flow voids (arrow) in the mural nodule. (c) Axial contrast-enhanced T1WI showing homogeneous enhancement of the mural nodule (arrow) and no enhancement of the cyst wall. (d) Axial diffusion-weighted image showing that the mural nodule (arrow) is low-intense. (e) A corresponding apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) map showing increased ADC of the nodule (arrow). The ADC value is 1.6 × 10−3 mm2/s. (f) Relative cerebral blood volume (rCBV) map showing increased relative CBV (rCBV) of the nodule. The rCBV ratio, defined as the maximal rCBV (enhanced lesion in yellow circle)/rCBV (contralateral normal white matter in red circle), is 12.42. (g) The intensity–time curve showing only a partial return to the baseline level (yellow line) due to massive leakage of contrast media into the interstitial space.