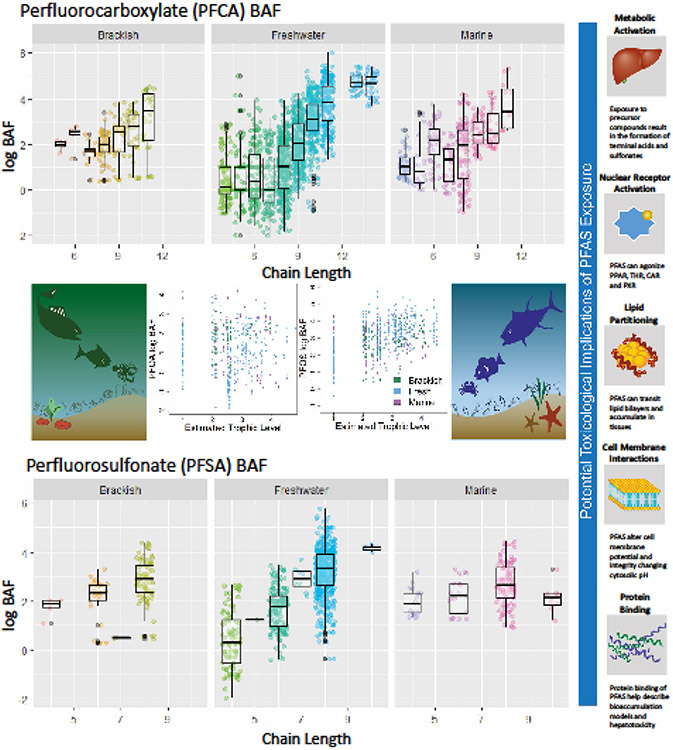
Fig. 5: Trophic transfer and environmental exposures:
Bioaccumulation factors (BAFs) in aquatic food webs are greater for long-chain perfluorocarboxylates (top panel) and perfluorosulfonates (bottom panel) than short-chains. Higher trophic-level organisms demonstrate greater bioaccumulation of PFOS than PFOA (center panel); trophic-level accumulation was estimated for data with a single-prey classification method (FishBase) and standardized bioaccumulation factor by wet weight of organism. Multiple toxicological implications (right panel) reflect the diversity of PFAS physicochemical properties and have been linked to both functional group and fluoroalkyl-carbon-chain length. Data were originally compiled by Burkhard (127).