Figure 1.
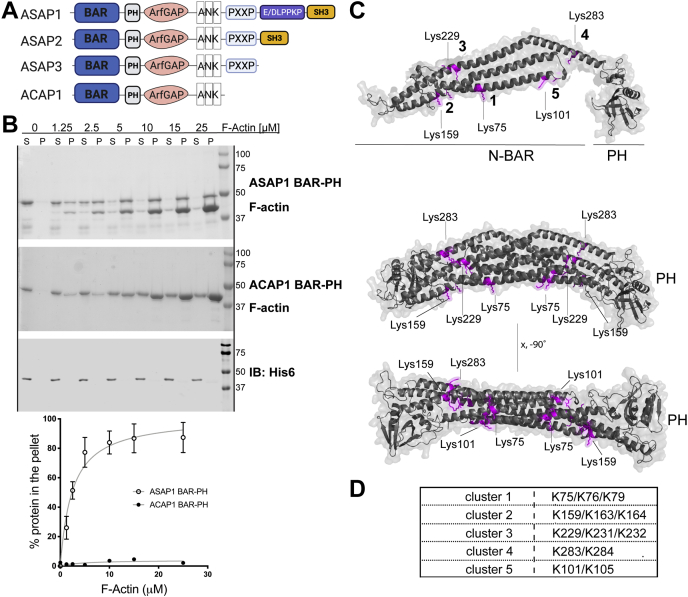
ACAP1 BAR-PH, unlike ASAP1 BAR-PH, does not bind to the actin filaments.A, schematic of the domain architecture of ASAP1, 2, 3, and ACAP1. B, results of the high-speed sedimentation assay for purified ASAP1 or ACAP1 BAR-PH in the absence or presence of increasing concentrations of actin filaments. Top panel shows increased pelleting of ASAP1 BAR-PH with increasing concentrations of F-actin, and middle (GelCode blue stained) and bottom (probed with anti-His6-antibody to identify ACAP1) panels show no pelleting of ACAP1 BAR-PH. The graph depicts quantification of all experiments. N = 3 independent experiments, mean ± SEM. C, surface ribbon representation of the homology model of ASAP1 BAR-PH highlighting lysine-rich clusters (numbered 1–5) in magenta. Top - monomeric representation of BAR-PH, middle and bottom - BAR-PH dimer rendering. Structure rendering was performed in PyMOL. D, lists residues belonging to each cluster. ANK, ankyrin repeats; BAR, Bin/Amphiphysin/Rvs domain; F-actin, filamentous actin; His6, 6x Histidine tag; IB, immunoblot; P, pellet; PH, pleckstrin homology; S, supernatant; SH3, Src homology 3 domain.