Figure 1. Homeostasis of HA, major constituent of ECM GAG.
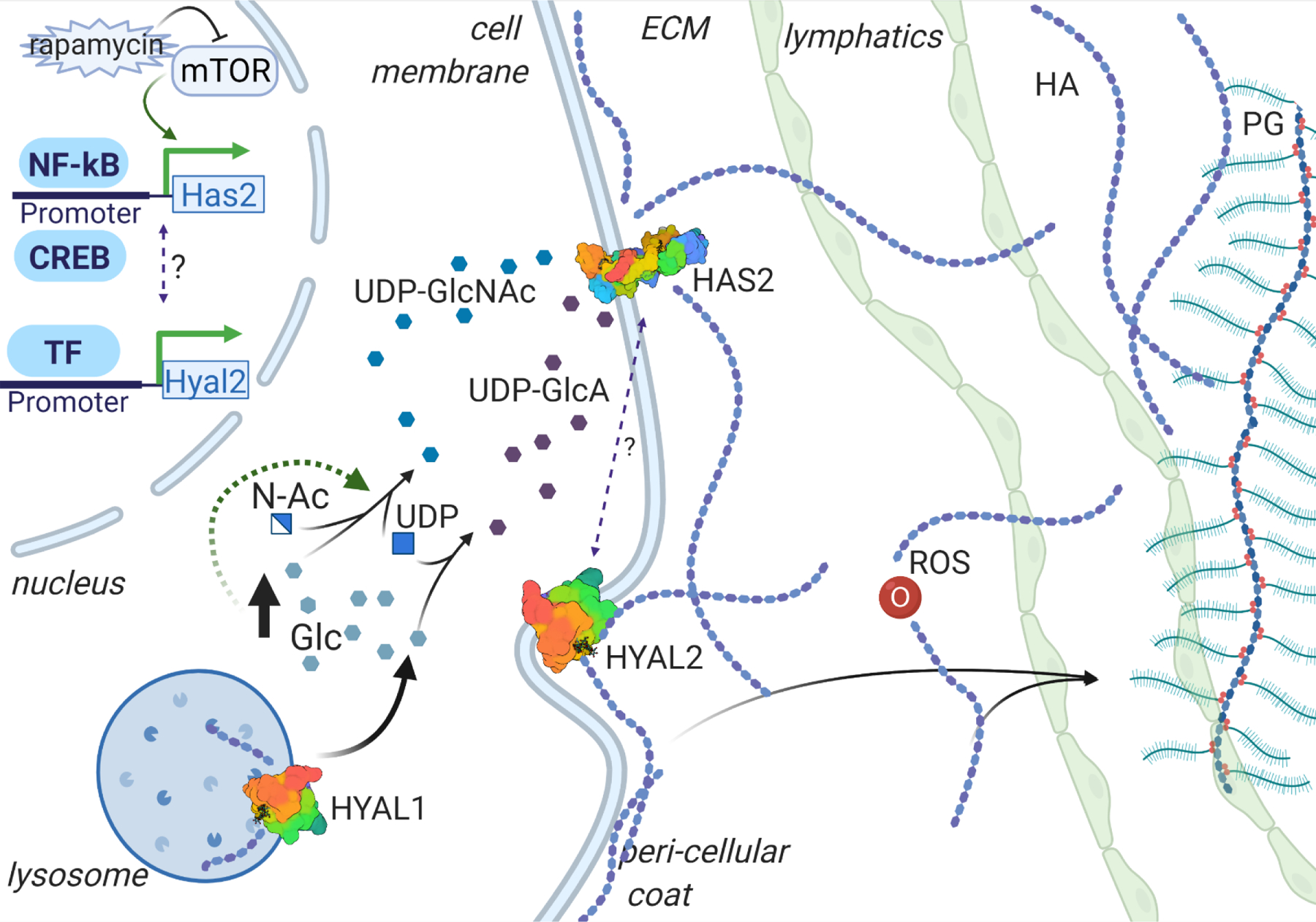
Hyaluronan synthases (HASs) are the enzymes responsible for hyaluronan (HA) anabolism, while hyaluronidases (HYALs) degrade the polymer extra- and intra-cellularly. Reactive Oxidative Species (ROS) are capable of degrading the HA molecules into polymers of random size. The regulation of HA synthesis and degradation is regulated by multiple pathways, including metabolic, growth, and inflammatory signaling. HA turnover involves uptake of the polymers of certain size into lymphatic tissue, and subsequent degradation in lymphatic and hepatic tissue. PG = Proteoglycan; Glc = glucose; N-Ac = N-acetyl; UDP-GlcNAc = UDP-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine, UDP-GlcA = UDP-D-glucuronic acid
