Figure 1. Visual representation of the conceptual framework for exploring patterns of peer vocalization in children with and without hearing loss.
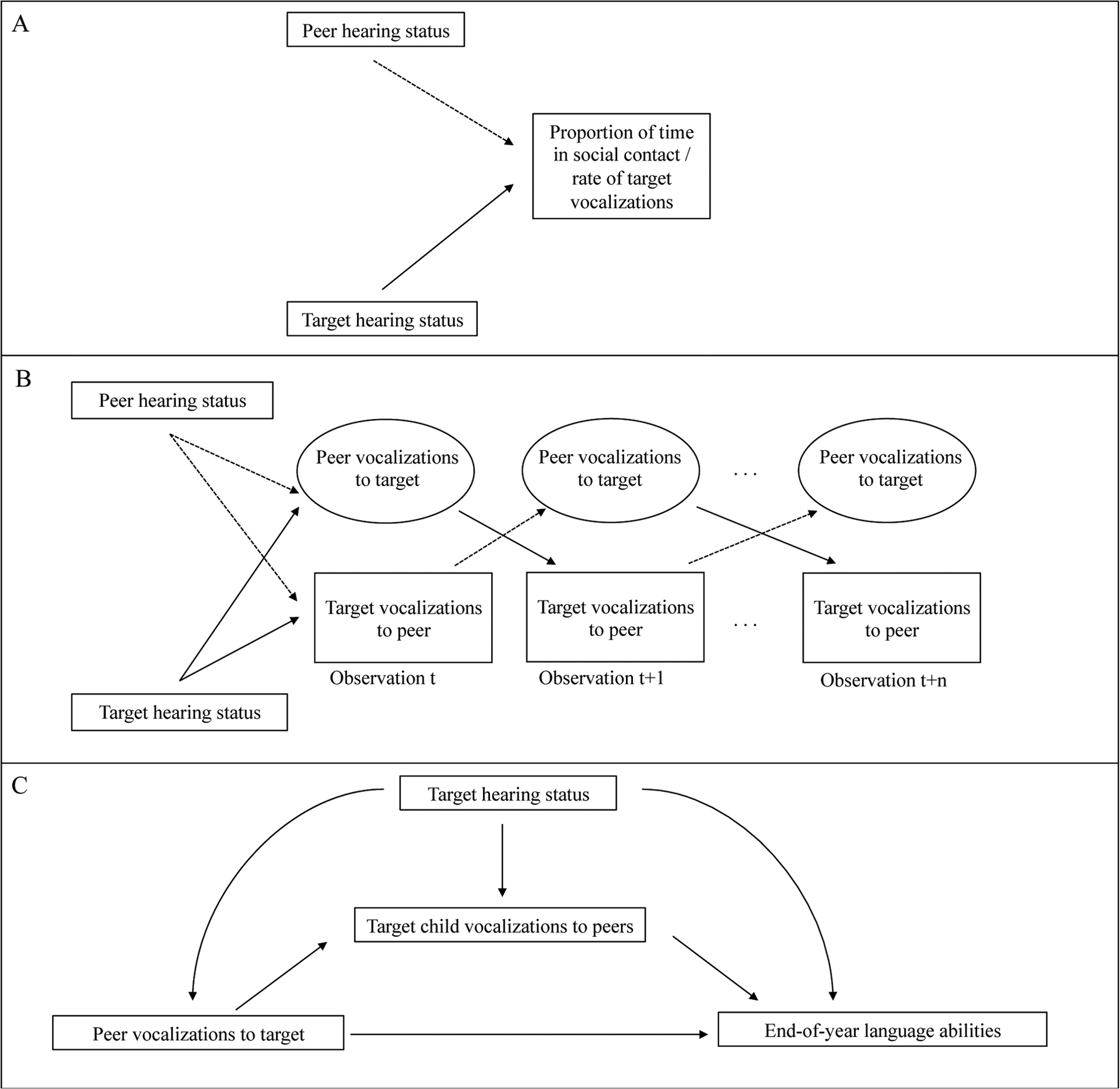
A) The top row depicts hypothesized influences of the target child and their peer’s hearing status (hearing loss or typical hearing) on both the proportion of time they spend in social contact and the rate of vocalizations that the target child makes to the peer. B) The middle row depicts hypothesized influences on the rate of vocalizations that the target child makes to the peer. Thus, the same associations are shown for peer vocalizations to highlight the reciprocal pattern of input and output over observations. C) The bottom row depicts hypothesized influences of hearing status on assessed language abilities and the direct and indirect associations between peer vocalizations and language abilities, mediated through target output.
