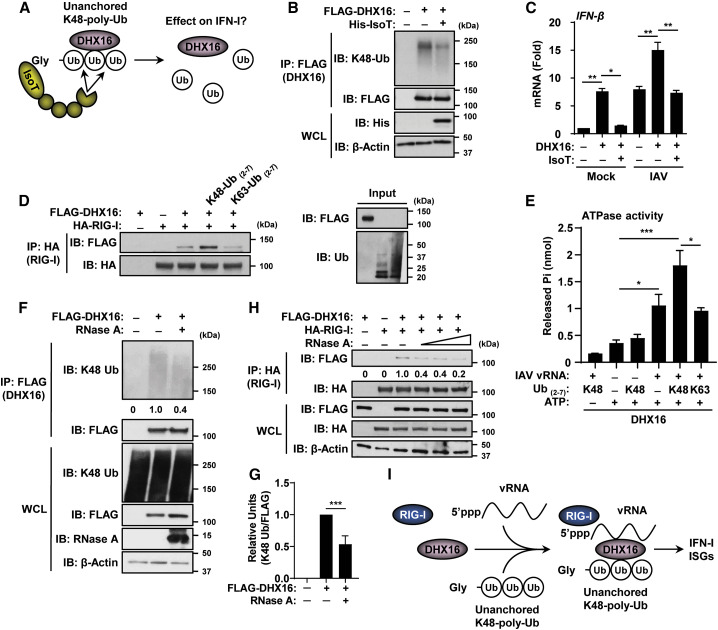
Figure 5.
DHX16 interacts with unanchored Ub and RNA to promote IFN-I production
(A) The IsoT de-ubiquitination assay.
(B) De-coupling of unanchored K48-poly-Ub from DHX16 following co-expression of IsoT in HEK293Ts (coIP).
(C) IFN-β expression following co-expression of DHX16 and IsoT in HEK293Ts infected with IAV for 24 h (PR8 MOI = 0.1) (qRT-PCR).
(D) In vitro interactions between DHX16 and RIG-I ± recombinant poly-Ub chains (coIP).
(E) Effects of recombinant poly-Ub (1 μg) and purified IAV vRNA (100 ng) on DHX16 ATPase activity in an in vitro ATPase assay.
(F) Interaction between DHX16 and unanchored K48-poly-Ub following co-expression in HEK293Ts in the presence of RNase A (100 μg/mL) (coIP).
(G) Immunoblot quantification of K48-Ub in (F) (densitometry).
(H) Interactions between DHX16 and RIG-I following co-expression in HEK293Ts in the presence of RNase A (0–100 μg/mL) (coIP).
(I) DHX16-RIG-I complex formation mediated through vRNA and unanchored poly-Ub.
Data are expressed as means (n = 3) ± SD. ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001 (one-way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparisons). Data are representative of 2–3 independent experiments.