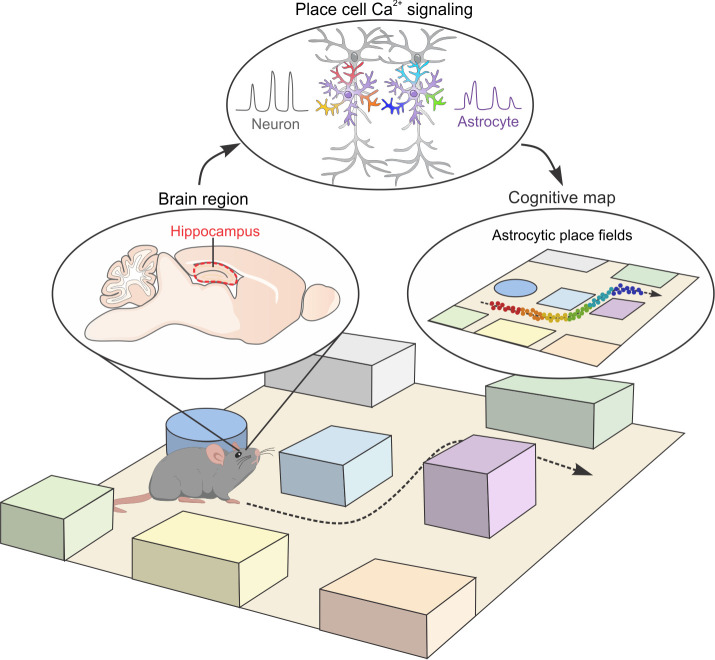
Fig 1. Cognitive map and underlying cellular mechanisms.
A cognitive map encodes spatial information and allows navigational planning. The hippocampus is a key structure containing cells responsible for constructing the cognitive map in the mammalian brain. Hippocampal neurons known as place cells become electrically active when the animal travels to specific locations within its environment. Using 2-photon in vivo Ca2+ imaging, Curreli and colleagues provide evidence that hippocampal astrocytes respond to spatial locations in a virtual reality environment with elevations in their intracellular Ca2+ signals. Moreover, the information contained by hippocampal astrocytes is not a passive copy of nearby neuronal information. The tantalizing unanswered question is whether astrocytes are active partners with neurons in generating a spatial cognitive map.