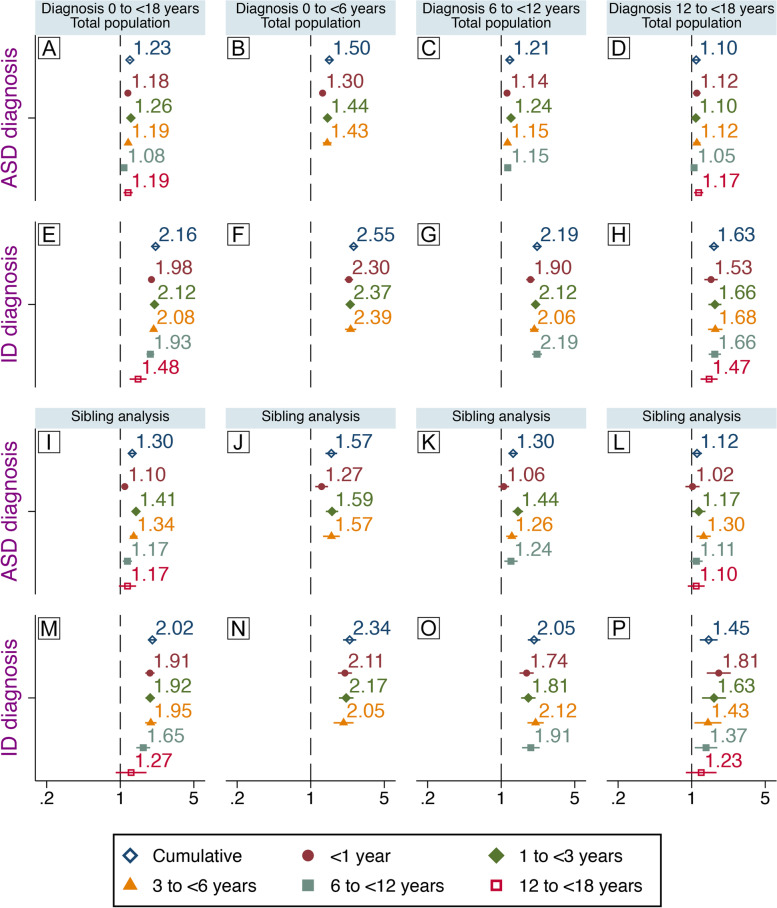
Fig. 2.
Infections during childhood and later diagnosis of ASD or ID. Associations between specialized care for infections during childhood and later, non-mutually exclusive, diagnosis of ASD and ID. Associations between exposure at different age intervals and diagnoses at different age intervals are also shown. Comparison between unrelated individuals in the general population are shown (A–H) and comparisons between full biological siblings (I–P). Hazard ratios presented here are from fully adjusted models. Population-based estimates (A–H) are adjusted for sex, parity, maternal body mass index, pre-eclampsia, parental age, education, income, region of origin, histories of psychiatric illness and infections, season of birth, gestational age at birth, size for gestational age, cesarean section, Apgar score. Estimates from the sibling analyses (I–P) are adjusted for sex, parity, gestational age at birth, and cesarean section