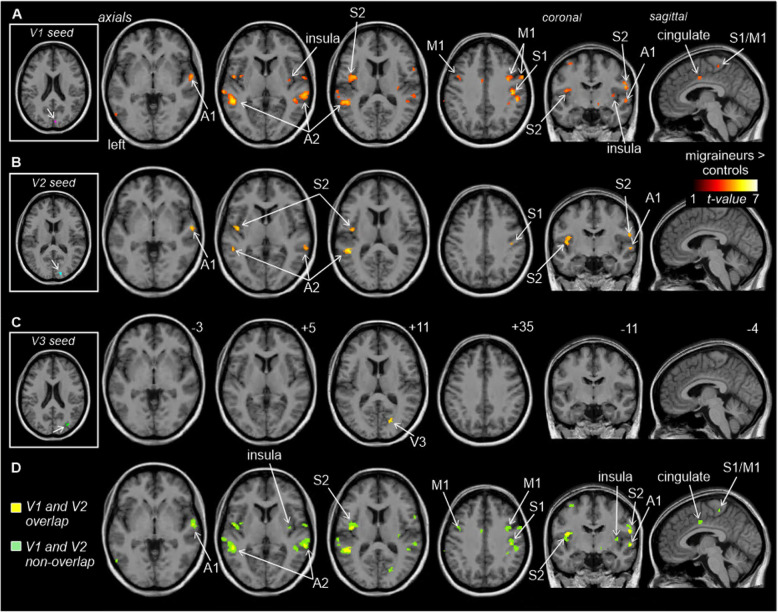
Fig. 2.
Significant differences in resting right V1, V2 and V3 connectivity between controls (n = 71) and migraineurs (n = 32) (random effects, p < 0.05, corrected). A. (left) An overlay of the right V1 seed extracted from the ALFF analysis (pink). Regions in which connectivity strength is significantly greater in migraineurs compared to controls overlaid on a mean T1-weighted anatomical image set. B. (left) An overlay of the right V2 seed (blue). Significant increased connectivity in migraineurs compared to controls, overlaid on a mean T1-weighted anatomical image set. C. (left) An overlay of the right V3 seed (green). Significant increased connectivity in migraineurs compared to controls, overlaid on a mean T1-weighted anatomical image set. D. Overlap (yellow) and non-overlap (green) of significant clusters in V1 and V2 functional connectivity analyses, overlaid on a mean T1-weighted anatomical image set. Location of each axial, coronal and sagittal slice in Montreal Neurological Institute (MNI) space is indicated at the top right of each slice. Slice locations are the same for all three seeds. A1: primary auditory cortex; A2: secondary auditory cortex; M1: primary motor cortex; S1: primary somatosensory cortex; S2: secondary somatosensory cortex; V1: primary visual cortex; V2: secondary visual cortex; V3: third visual complex