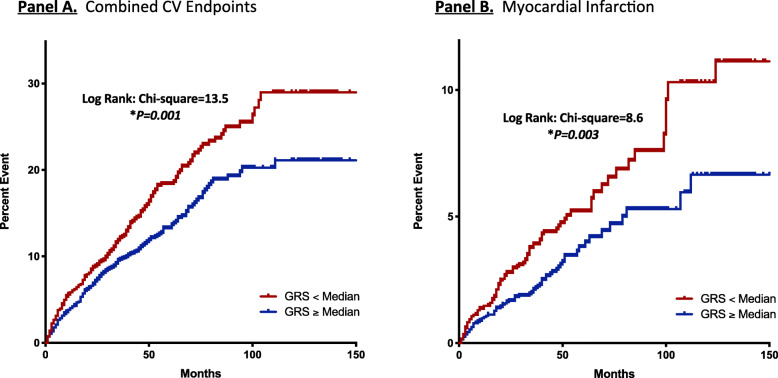
Fig. 1.
Cumulative hazards stratified by genetic vitamin D exposure for pre-specified clinical endpoints in hypertensive-diabetic subjects. Cumulative hazards curves supplemented with data on events-free survival. A Vitamin D genetic risk score (GRS) predicted combined cardiovascular (CV) endpoints in hypertensive subjects: mean survival (Below median: 123.6 [95%CI 119.8 to 127.5] months, versus ≥ median: 131.8 [95%CI 128.8 to 134.9] months, log-rank = 13.5, P<0.001); B Vitamin D GRS predicted incident myocardial infarction (MI): mean survival (below median: 145.1 [95%CI 142.6 to 147.7 months], versus ≥ median: 149.2 [95%CI 147.4 to 151.0 months], log-rank = 8.6, P = 0.003)