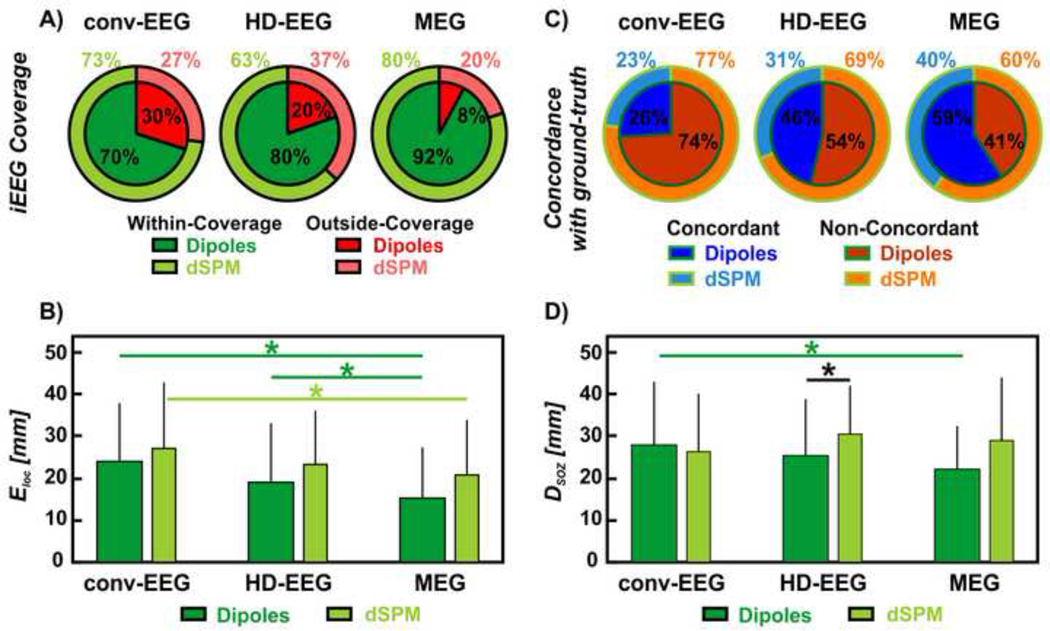
Figure 4. Non-invasive localization of IEDs (dipoles and dSPM) against ground-truth IZ and SOZ.
(A) Red wedges correspond to the proportion of IEDs localized outside iEEG coverage; green wedges correspond to the proportion of IEDs localized within the iEEG coverage. The inner wedges are for dipoles; the outer wedges are for dSPM. (B) Localization error (Eloc) of conv-EEG, HD-EEG and MEG with respect to the ground-truth IZ (in mm) for both dipoles and dSPM. Difference in Eloc was regarded as significant (*) when the p-value was < 0.05. (C) Blue wedges correspond to the proportion of IED sources concordant with the ground-truth IZ at the gyral-width level (out of all the within-coverage sources) or precision. The orange wedges correspond to the IED sources non-concordant with the ground-truth IZ. The inner wedges are for dipoles; the outer wedges are for dSPM. (D) Distance from SOZ (DSOZ) of conv-EEG, HD-EEG and MEG with respect to the ground-truth IZ (in mm) for both dipoles and dSPM.