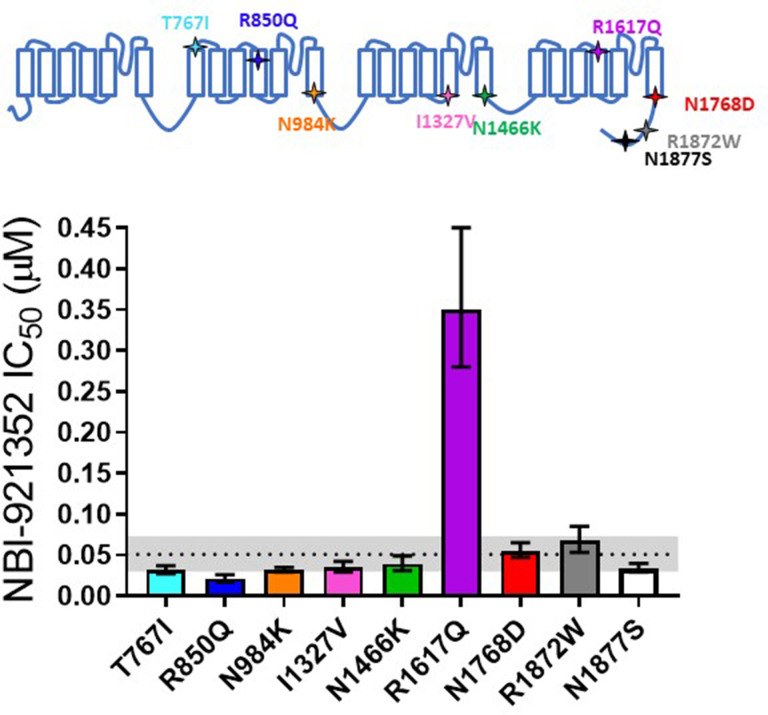
Figure 2. Comparison of NBI-921352 potency on human wild-type NaV1.6 and patient-identified variants of NaV1.6.
All constructs were transiently transfected into Expi293F cells and evaluated by automated patch-clamp electrophysiology using the SophionQube. The voltage-clamp methods were identical to those used for evaluation of the wild-type channels. The error bars indicate the 95% confidence interval of the fitted IC50 generated in Prism. The horizontal dotted line is at the IC50 for wild type NaV1.6 (51 nM, see Figure 1). The gray shaded band indicates the 95% confidence range for the IC50 for wild-type NaV1.6. Only two variants have fitted IC50’s outside of the 95% confidence interval for the wild-type channel IC50. R850Q was slightly more potently inhibited and R1617Q was less potently inhibited than the wild-type channel. R1617Q is near the proposed binding site for NBI-921352.