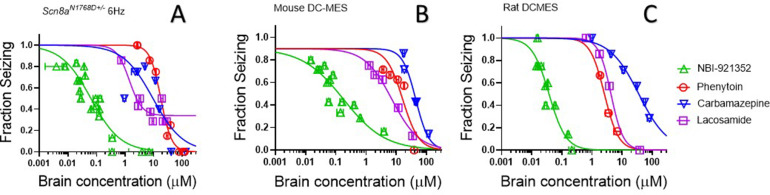
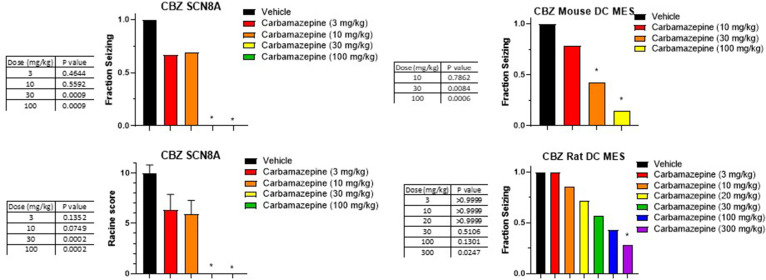
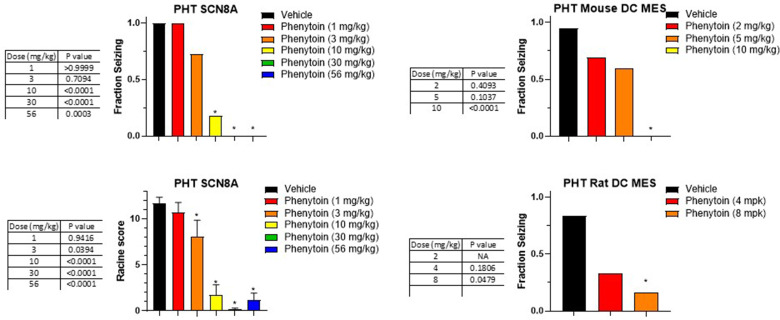
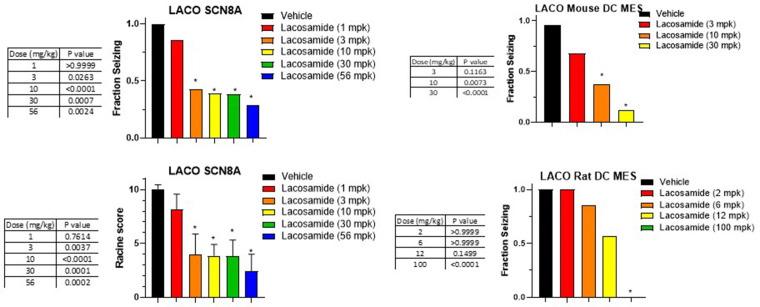
Figure 6. NBI-921352 is more potent than three commonly prescribed NaV inhibitor ASMs.
Brain concentration versus fraction of animals exhibiting is plotted for NBI-921352 versus that for phenytoin, carbamazepine, and lacosamide in the Scn8aN1768D+/- modified 6 Hz model (A), the wild-type mouse DC-MES model (B), and the wild-type rat DC-MES model (C). Each point represents the fraction of animals exhibiting a GTC with hindlimb extension after stimulus from a dosing group of six to eight animals. Horizontal error bars show the standard error of the mean brain concentrations measured from the animals in that dosing group immediately after assay. Where error bars are not visible, they are smaller than the symbols. Statistical analysis of significance of the dose groups for the concentrations shown were performed as in Figure 5 and can be found in Figure 5—figure supplement 1 (NBI-921352), Figure 6—figure supplement 1 (Carbamazepine), Figure 6—figure supplement 2 (Phenytoin), and Figure 6—figure supplement 3 (Lacosamide).