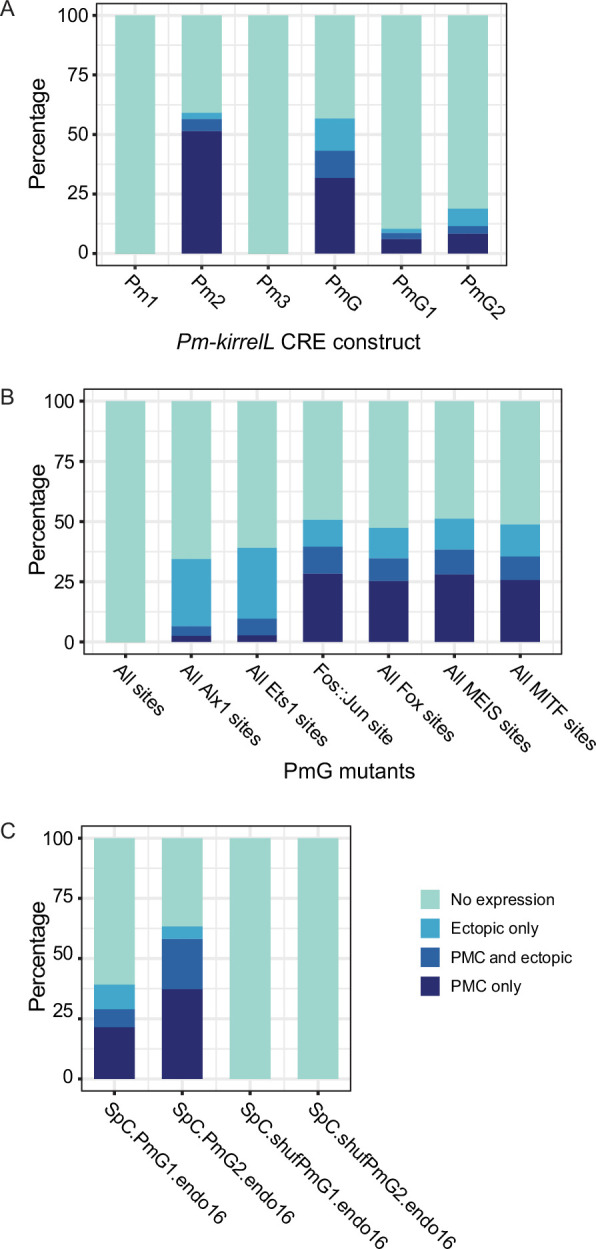
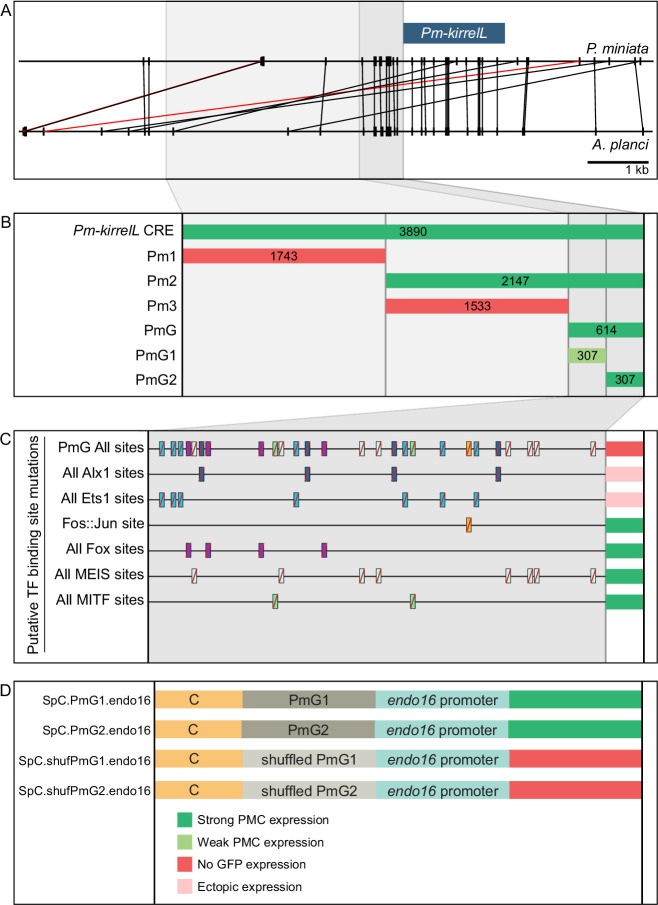
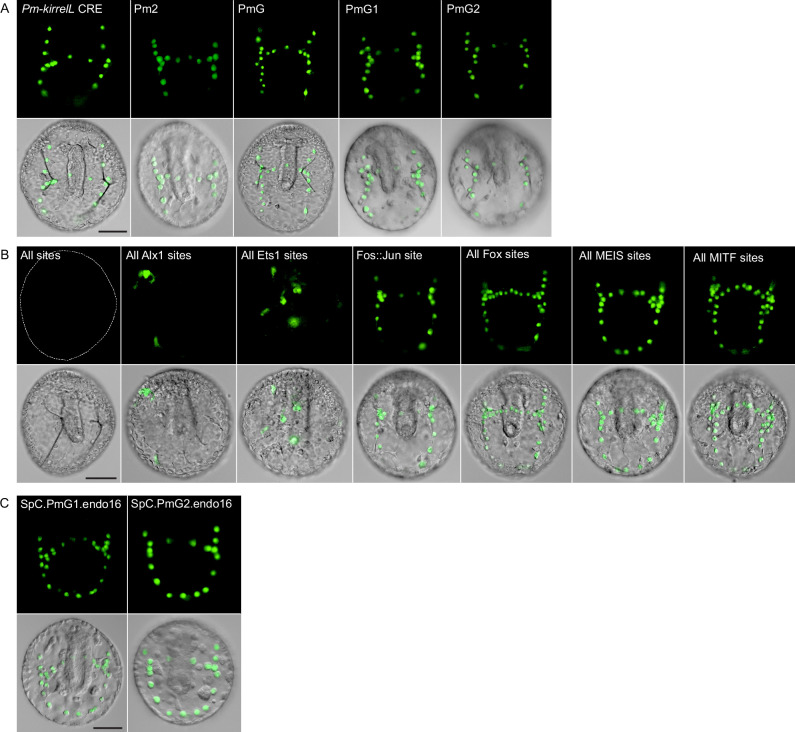
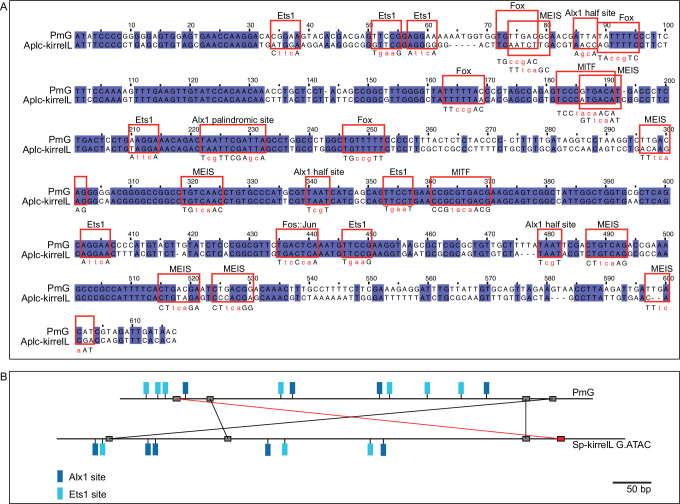
Figure 7. Functional analysis of noncoding genomic sequences upstream of Pm-kirrelL to identify cis-regulatory elements (CREs).
(A) Phylogenetic footprinting of genomic sequences near P. miniata and A. planci kirrelL using GenePalette. Black lines indicate identical sequences of 13 bp or longer in the same orientation while red lines indicate identical sequences of 13 bp or longer in the opposite orientation. (B) Summary of GFP expression regulated by noncoding sequences upstream of the Pm-kirrelL translational start site. (C) Summary of GFP expression driven by PmG element mutants. (D) Summary of GFP expression regulated by chimeric reporter constructs containing Sp-kirrelL element C and Pm-kirrelL G1 or G2 elements. Criteria for strong and weak primary mesenchyme cell (PMC) expression are defined in Figure 2. Ectopic expression is defined as majority of injected embryos exhibiting GFP expression in cells other than PMCs.
Figure 7—figure supplement 1. Sea star Pm-kirrelL cis-regulatory element (CRE) truncation and mutational analysis.
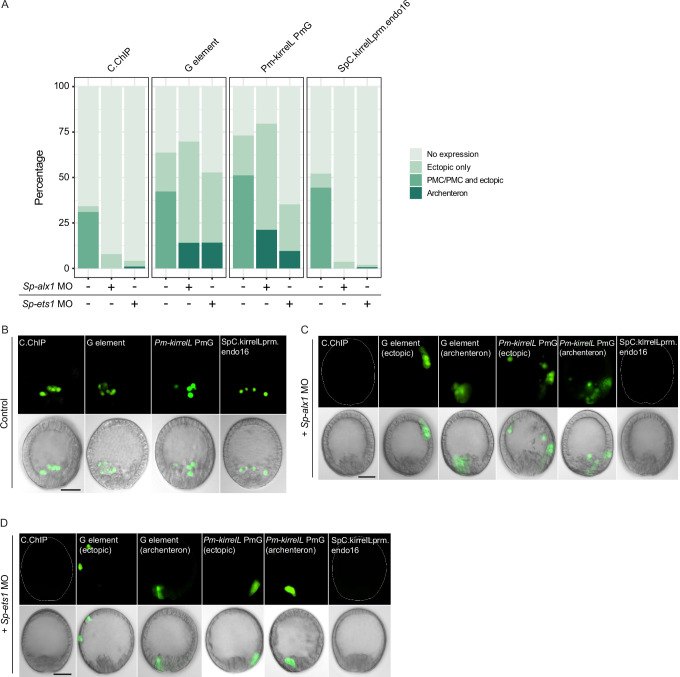
Figure 7—figure supplement 2. Stacked bar plots showing summary of GFP expression patterns of injected embryos scored at 48 hpf.