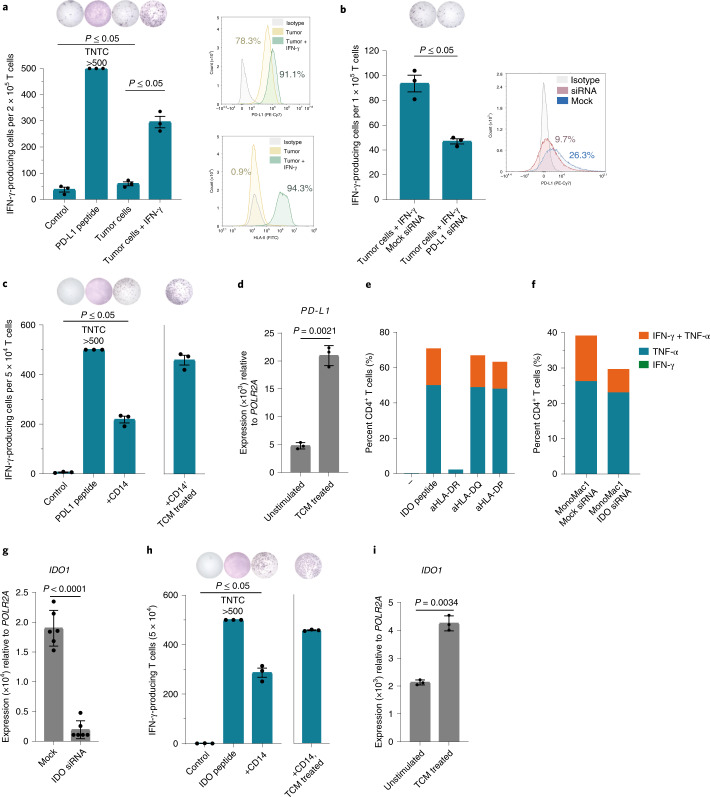
Fig. 4. PD-L1- and IDO-specific T cells from vaccinated patients react against PD-L1- and IDO-expressing target cells.
a, Left, PD-L1-specific T cell culture (MM1636.05) reactivity against PD-L1 peptide or autologous tumor cells in the IFN-γ ELISPOT assay. Tumor cells were either not treated or pretreated with 200 U ml−1 IFN-γ for 48 h before the assay. Effector:target (E:T) ratio of 10:1 was used. Right, PD-L1 and HLA-II surface expression on melanoma cells with (green) or without (yellow) pretreatment with IFN-γ compared to an isotype control (gray) as assessed by flow cytometry. b, Left, PD-L1-specific T cell (MM1636.05) reactivity in the IFN-γ ELISPOT assay against autologous tumor cells pretreated with IFN-γ (500 U ml−1) and transfected with mock or PD-L1 small interfering (si)RNA 24 h after transfection. E:T ratio, 10:1. Right, PD-L1 surface expression on melanoma tumor cells (MM1636.05) assessed by flow cytometry 24 h after transfection with mock (blue) or PD-L1 (red) siRNA compared to the isotype control (gray). c, Reactivity of the CD4+ PD-L1-specific T cell clone (MM1636.14) against PD-L1 peptide or autologous CD14+ cells; E:T ratio, 10:1. CD14+ cells were isolated using magnetic bead sorting and used as targets in an ELISPOT assay directly or after pretreatment for 2 d with TCM derived from the autologous tumor cell line. d, Quantitative PCR with reverse transcription (RT–qPCR) analysis of PD-L1 (CD274) expression in sorted CD14+ cells before and after treatment with autologous TCM for 48 h. e, Reactivity of the IDO-specific CD4+ T cell clone (MM1636.23) against IDO peptide combined with HLA-DR (L243)-, HLA-DQ (SPV-L3)- or HLA-DP (B7/21)-blocking antibodies (aHLA-DR, aHLA-DQ and aHLA-DP) in an intracellular staining assay (ICS) for IFN-γ and TNF-α production. T cells were incubated with individual blocking antibodies (2 μg ml−1) for 30 min before adding IDO peptide. f, Reactivity of the IDO-specific CD4+ T cell clone (MM1636.23) against the HLA-DR-matched IDO-expressing cell line MonoMac1 transfected with mock or IDO siRNA in an ICS assay, E.T ratio, 4:1. siRNA transfection was performed 48 h before the experiment. g, RT–qPCR analysis of IDO1 expression in MonoMac1 cells 48 h after siRNA transfection. h, Reactivity of the CD4+ IDO-specific T cell clone (MM1636.14) against IDO peptide or autologous CD14+ cells; E:T ratio, 20:1. CD14+ cells were isolated using magnetic bead sorting and used as targets in an ELISPOT assay directly or after pretreatment with TCM derived from the autologous tumor cell line. i, RT–qPCR analysis of IDO1 expression in sorted CD14+ cells before and after treatment with autologous TCM for 48 h. Bars in RT–qPCR data (d,g,i) represent the mean of three (d,i) or six (g) technical replicates ±s.d.; P values were determined by two-tailed parametric t-tests. ELISPOT counts (a,b,c,h) represent the mean value of three technical replicates ±s.e.m.; response P values were determined using the distribution-free resampling (DFR) method. TNTC, too numerous to count.