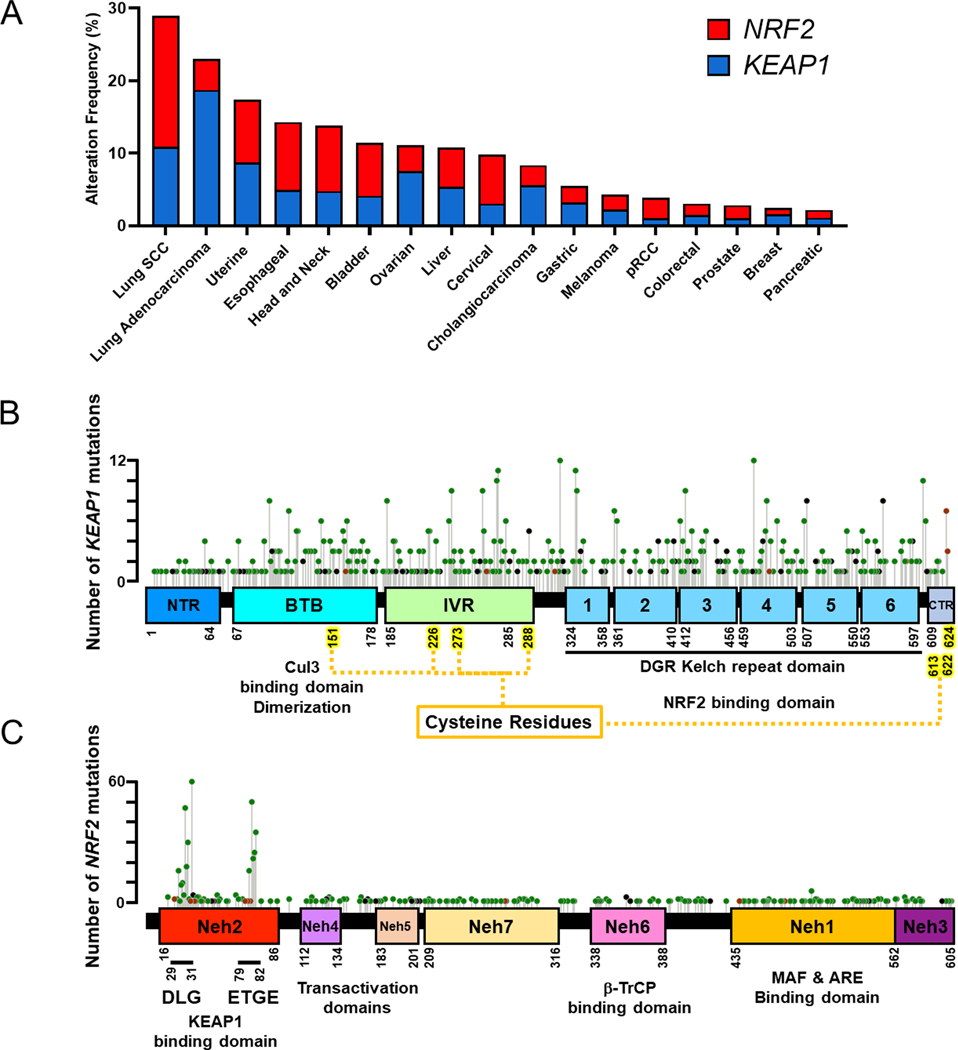
Figure 2: Mutation Spectrum in the KEAP1/NRF2 Pathway.
A) Frequency of mutations in NRF2 and KEAP1 in solid tumors generating using cBioportal TCGA data.
B) Map of KEAP1 with mutations based on cBioportal TCGA datasets. KEAP1 is divided up into the following domains: NTR, BTB, IVR, 6 Kelch domains, and CTR. Key cysteine residues for sensing ROS and toxins are indicated.
C) Map of NRF2 with 7 Neh domains and mutations labelled. The KEAP1 binding motifs, DLG and ETGE, are indicated in the Neh2 domain, while the loci of phosphorylation by β-TrCP is located in the Neh6 domain. Somatic mutations in NRF2 are highly concentrated in DLG and ETGE motifs.
SCC, squamous cell carcinoma; pRCC, papillary renal cell carcinoma; KEAP1, Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1; NRF2, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; NTR, N terminal region; BTB, Bric-a-brac; IVR, intervening region; DGR, double glycine repeat; CTR, C terminal region; Maf, musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma; ARE, antioxidant response element