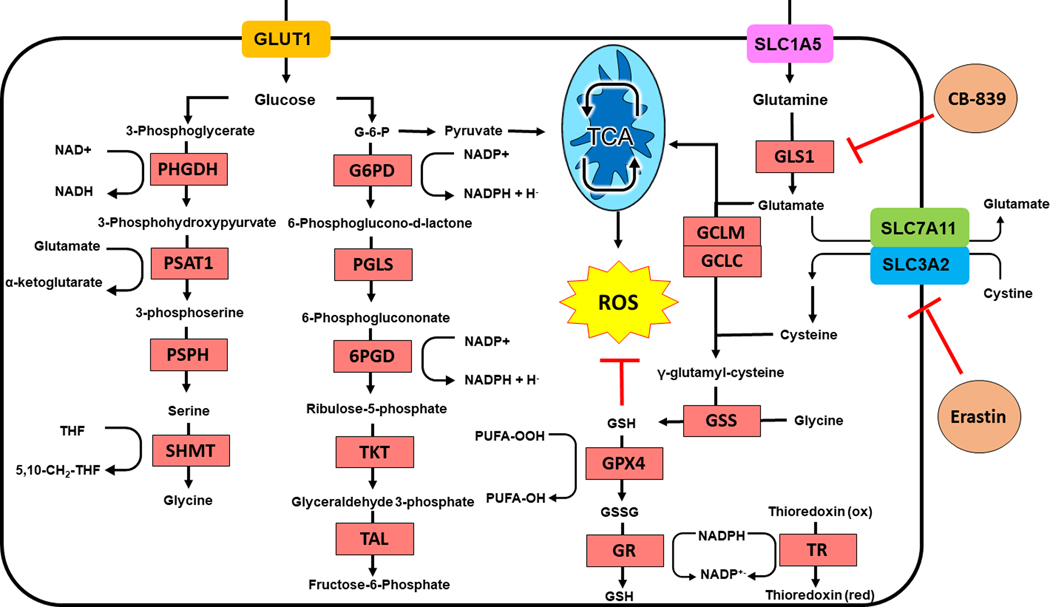
Figure 3: Metabolic Rewiring by NRF2.
Activation of NRF2 dramatically enhances generation of glutathione by increasing synthesis of glutathione from intracellular glutamate, cysteine, and glycine. Intracellular glutamate is derived from glutamine through GLS-1. Cystine is imported by the NRF2 target SLC7A11. Serine and glycine are synthesized via NRF2 dependent processes. NADPH is synthesized to support redox metabolism by the pentose phosphate pathway. GLS-1 and SLC7A11 function can be impaired by CB-839 and erastin respectively.
PHGD, phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase; PSAT1, phosphoserine aminotransferase; PSPH, phosphoserine phosphatase; SHMT, serine hydroxymethyltransferase; G6PD, glucose-6-phopshate dehydrogenase; PGLS, 6-phosphogluconolactonase; 6PGD, 6-phosphogluctonate dehydrogenase; TKT, transketolase; TAL, transaldolase; GPX4, glutathione peroxidase 4; GR, glutathione reductase; GLS1, glutaminase 1; GCLC, glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic subunit; GCLM, glutamate-cysteine ligase modifier subunit; GSS, glutathione synthetase; TR, thioredoxin; NAD(P)H, nicotinic adenine dinucleotide (phosphate); PUFA, polyunsaturated fatty acid; THF, tetrahydrofolate