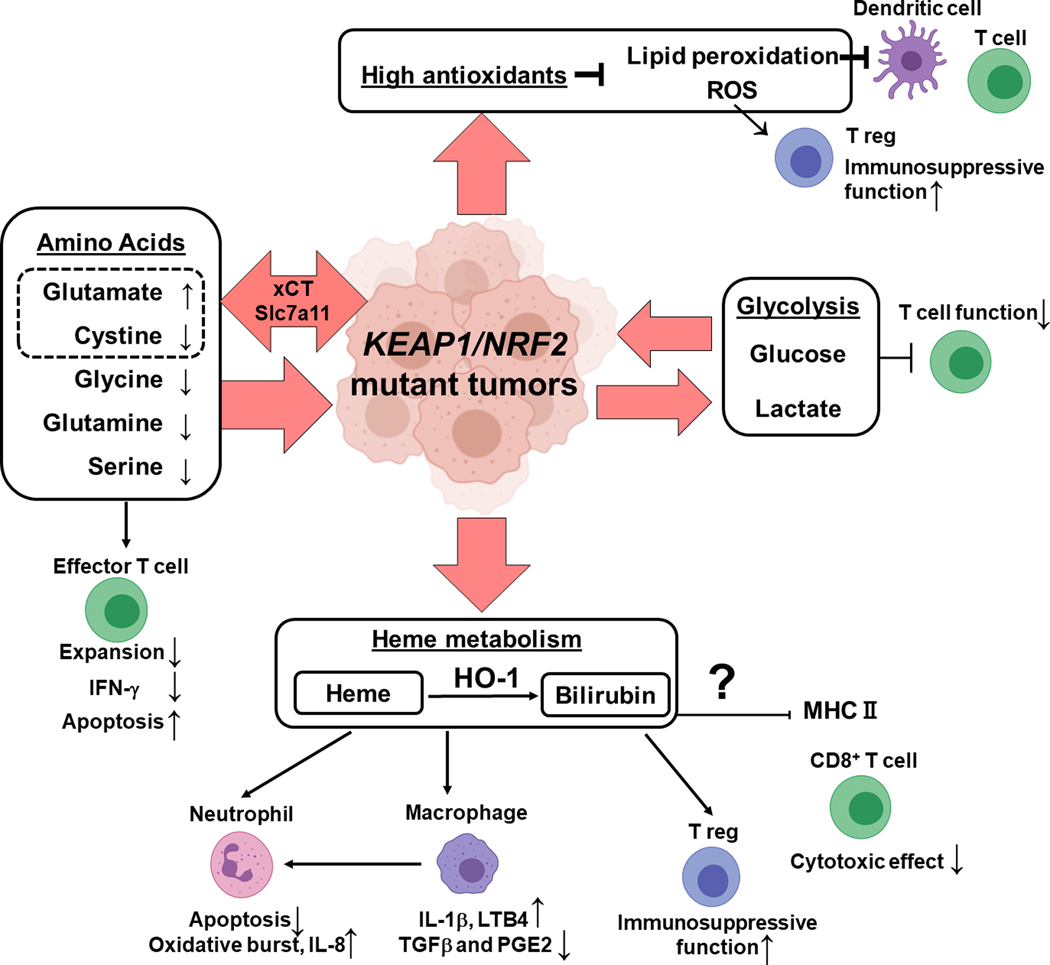
Figure 5: Impact of Keap1/Nrf2 Mutation on Tumor Microenvironment and Anti-tumor Immune Responses.
Keap1 LOF/ Nrf2 GOF mutation harboring tumors display increased uptake of non-essential amino acids such as glycine, serine, and glutamine. Cystine is imported through NRF2 regulated transporter xCT. Overall, in the microenvironment of Keap1/Nrf2 mutant tumors, glutamate is increased while cystine, glycine, glutamine, serine is depleted These metabolic changes can inhibit effector T cell function (expansion, production of IFN-γ) and induce apoptosis. Besides amino acids, Keap1/Nrf2 mutations result in increased glycolysis and thus increased glucose consumption and lactate secretion which can be deleterious for T cell function. NRF2 is a master regulator of antioxidants that decrease ROS and lipid peroxides which can impact dendritic cells, T cell effector cells and T regulatory cells. Hyperactivation of NRF2 results in altered heme metabolism and the byproducts of these pathways can impact neutrophils, macrophages, T regulatory cells and cytotoxic T lymphocytes.