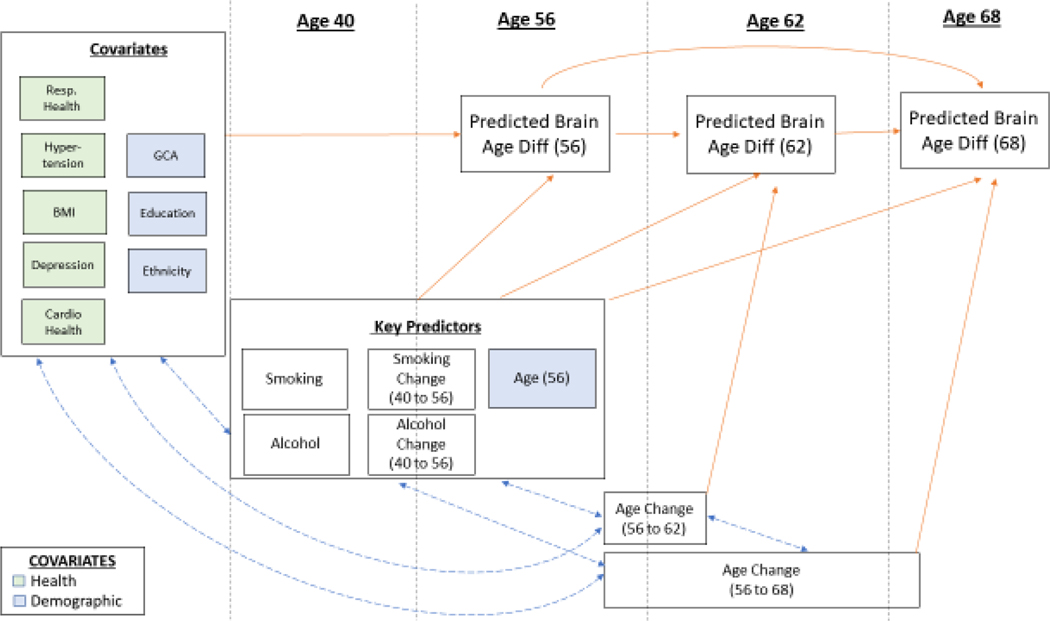
Figure 2.
Measures in Model 2: Smoking and Alcohol Predicting PBAD, with Covariates. Abbreviations: GCA=General Cognitive Ability; Resp=Respiratory; BMI=body mass index; Diff=difference. GCA, education, ethnicity, respiratory health, hypertension, BMI, cardiovascular health, and depression were correlated with each other. Key predictors (smoking, smoking change [age 40 to 56], alcohol consumption, and alcohol consumption change [age 40 to 56]) were correlated with each other. Age change at 56 to 62 and 56 to 68 were correlated with each other. Then, covariates, key predictors, and age change intercorrelations were modeled. Age 56 PBAD was regressed onto covariates. All three PBAD scores were regressed onto key predictors. Age 62 PBAD was regressed onto age change (56 to 62), and age 68 PBAD was regressed onto age change (56 to 68). Age 68 PBAD was regressed onto both age 56 PBAD and age 62 PBAD, and age 62 PBAD was regressed onto age 56 PBAD.