Figure 4. Pfcrisp− parasites grow normally as asexuals and undergo gametocytogenesis.
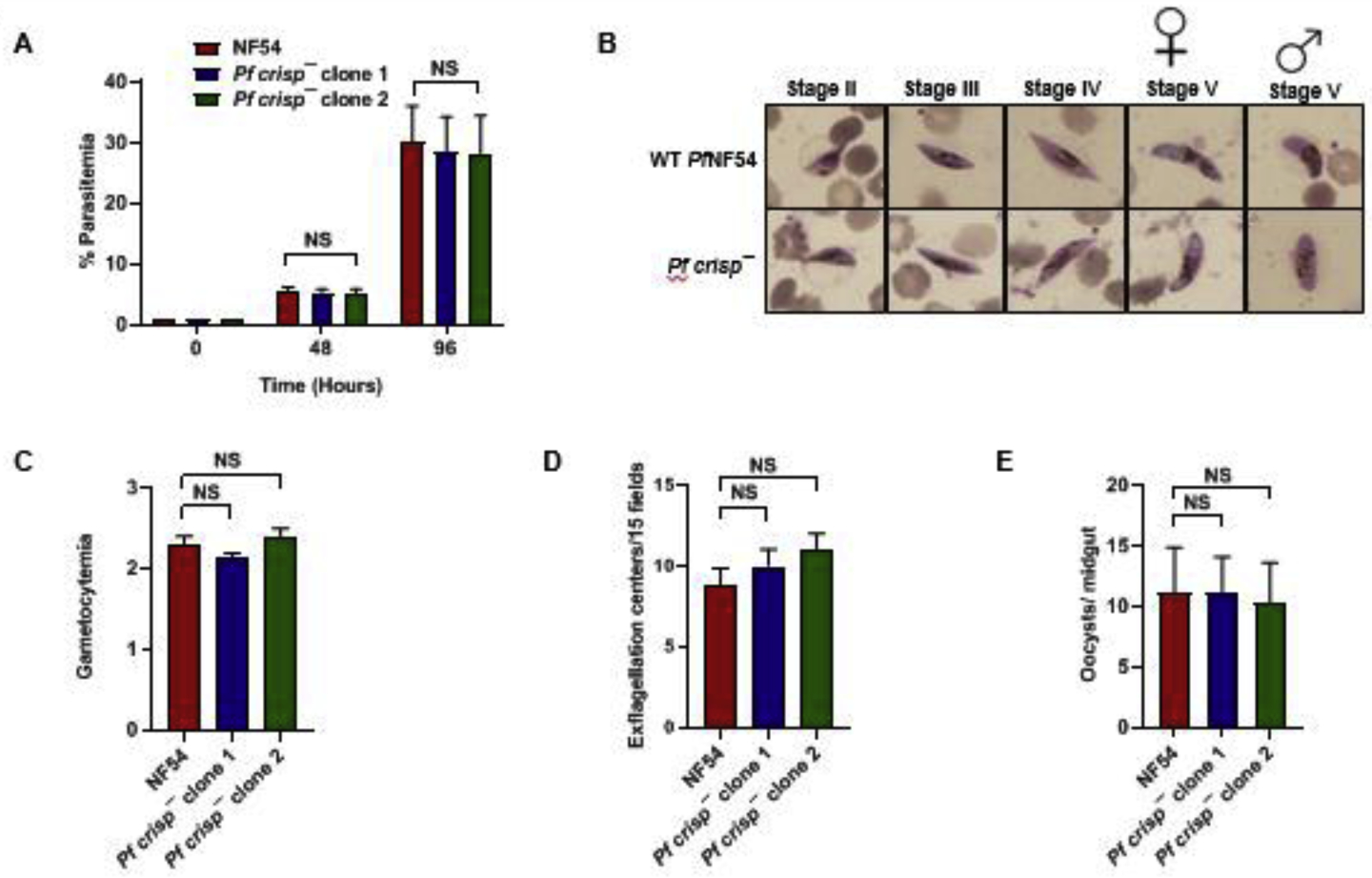
(A) Ring stage synchronous cultures for WT PfNF54 and Pfcrisp− (clone 1 and 2) were set up at 1% parasitemia and parasite growth was measured over the course of two erythrocytic cycles using Giemsa-stained smears. Data were averaged from three biological replicates and presented as the mean ± standard deviation (SD). (B) Day 15 gametocytemia for WT PfNF54 and Pfcrisp− (clone 1 and 2) was measured using Giemsa-stained smears. Data were averaged from three biological replicates and presented as the mean ± standard deviation (SD). (C) Number of exflagellation centers per field at 15 min post-activation WT PfNF54 and Pfcrisp− (clone 1 and 2). Data were averaged from three biological replicates and presented as the mean ± standard deviation (SD). (D) Oocysts per mosquito midgut were enumerated on day 7 post feed for WT PfNF54 and Pfcrisp− (clone 1 and 2) fed mosquitoes. Data were averaged from three biological replicates with a minimum of 50 mosquito guts and presented as the mean ± standard deviation (SD). NS-Not significant.
