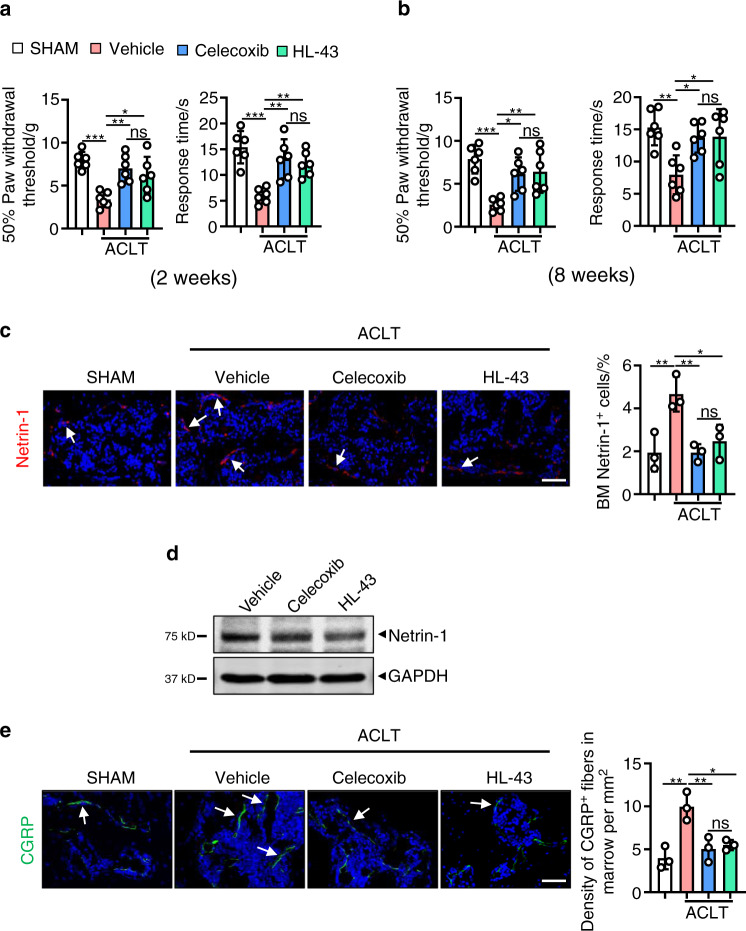
Fig. 6.
HL-43 reduces pain in OA by suppressing Netrin-1 secretion by osteoclasts and CGRP-positive sensory neuron recruitment to subchondral bone. Von Frey assay and thermal hyperalgesia test conducted at the right hind paw of the WT mice treated with celecoxib (30 mg·kg−1) or HL-43 (30 mg·kg−1) for 2 weeks (a) or 8 weeks (b) after ACLT surgery. Error bars are the mean ± s.d. **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001, ns, not significant by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s t tests. n = 6 for each group. c Representative images of IHF staining of Netrin-1 (red) in the subchondral bone of the WT mice orally treated with celecoxib (30 mg·kg−1) or HL-43 (30 mg·kg−1) 2 weeks post-ACLT surgery (left) and quantitative analysis (right). The white arrows indicate Netrin-1 IHF signals. Error bars are the mean ± s.d. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001, ns, not significant by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s t tests. n = 3 for each group. Scale bars, 20 μm. d Representative images of Netrin-1 protein expression by western blotting for osteoclasts generated using BMMs from WT mice stimulated with 10 ng·mL−1 M-CSF and 50 ng·mL−1 RANKL. The cells were incubated with 100 nmol·L−1 PGE2 with or without celecoxib (10 μmol·L−1) or HL-43 (10 μmol·L−1) for 5 days. The experiments were performed with three biological replicates. e Representative images of IHF staining of CGRP-positive sensory nerve fibers (red) in the subchondral bone of the WT mice orally treated with celecoxib (30 mg·kg−1) or HL-43 (30 mg·kg−1) 2 weeks post-ACLT surgery (left) and quantitative analysis (right). The white arrows indicate CGRP IHF signals. Error bars are the mean ± s.d. **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001, ns, not significant by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s t tests. n = 3 for each group. Scale bars, 20 μm