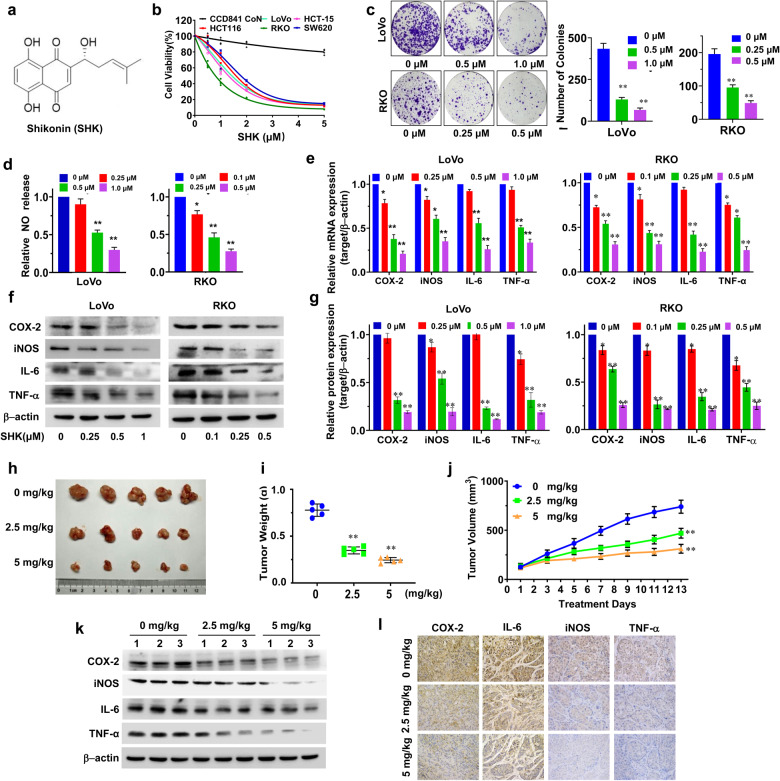
Fig. 1.
Effect of shikonin on the malignant phenotypes of human colorectal cancer cells. a Chemical structure of shikonin (SHK). b Colorectal cancer cells (LoVo, RKO, HCT-15, HCT-116, and SW620) and normal human colonic epithelial cells (CCD841 CoN) were cultured with the indicated concentrations of SHK for 48 h, after which the cell viability was determined using the CCK-8 assay. c The SHK-induced reduction of colony formation was analyzed, and the colony formation numbers were calculated. d The NO content following SHK treatment was determined using the Griess reagent. LoVo and RKO cells were cultured with SHK. The expression of inflammatory markers (COX-2, iNOS, IL-6, and TNF-α) was analyzed by qPCR (e) and western blotting (f). A quantitative analysis of these proteins was also performed (g). The data are presented as the means ± SD of at least three separate experiments. (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, SHK treatment group vs. vehicle control group). In vivo antitumor efficacy of SHK in a LoVo xenograft tumor model. Tumor appearance (h), total tumor weights (i) and tumor volumes (j) were assessed. The expression of inflammatory markers (COX-2, iNOS, IL-6, and TNF-α) in tumor tissues was analyzed by western blotting (k) and immunohistochemical analysis (l). Data were presented as the means ± SD from n = 5 mice/group. (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, SHK treatment group vs. vehicle control group. Magnification, ×200)