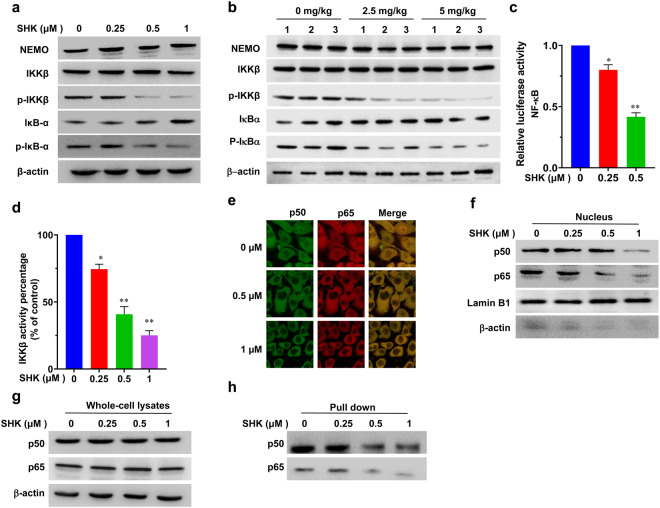
Fig. 3.
Effect of SHK on NEMO/IKKβ/NF-κB signaling. a The protein levels of NEMO, p-IKKβ/IKKβ, and p-IκBα/IκBα in LoVo cells treated with the indicated doses of SHK were analyzed by western blotting. b The protein levels of NEMO, p-IKKβ/IKKβ, p-IκBα/IκBα protein in tumor tissues were analyzed by western blotting. c LoVo cells were co-transfected with pNFκB-luc containing a Renilla luciferase reporter (as internal control) for 24 h and then treated with SHK for 48 h. Luciferase activity was determined using a dual-luciferase reporter assay system. d The IKKβ kinase activity was assessed using a spectrophotometric quantitative detection kit in LoVo cells. The relative activity was calculated using the provided formula. e The subcellular localizations of p50/p65 in LoVo cells following 48 h of treatment with SHK was examined by confocal microscopy analysis. The protein levels of p65 and p50 in nucleus (f) and whole-cell lysates (g) were measured by western blot analysis. Lamin B1 and β-actin were used as controls for sample loading. h The binding of p65 and p50 to a COX-2 promoter probe was analyzed using a streptavidin-agarose pull-down assay. The data are presented as the means ± SD of at least three separate experiments. (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, SHK treatment group vs. vehicle control group)