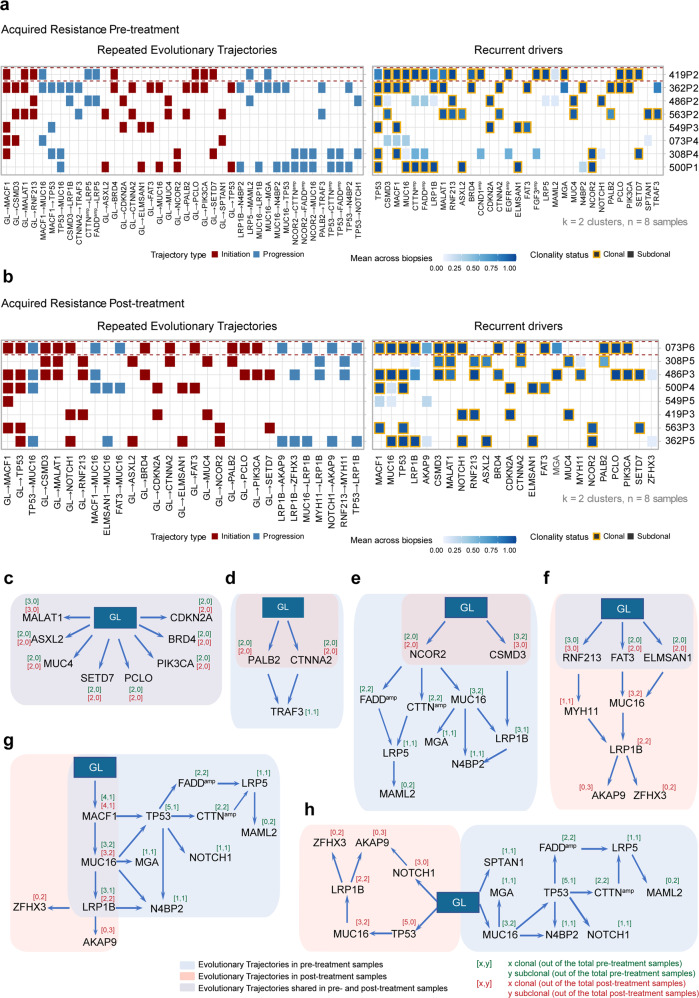
Fig. 5.
Repeated evolutionary trajectories of acquired cetuximab resistance in HNSCCs. a, b REVOLVER analysis of pre-treatment samples (a) and post-treatment samples (b) from acquired resistance group. The left heatmap shows the most common repeated evolutionary trajectories, and the right heatmap shows the average proportion of samples bearing the alteration for the most recurrent putative driver genes (on the basis of presence/absence). c Repeated evolutionary trajectories unchanged before and after cetuximab administration. d, e Repeated evolutionary trajectories retained only the early transition after cetuximab administration. f Repeated evolutionary trajectories with early transitions extended after cetuximab administration. g Cetuximab retained the backbone of the repeated evolutionary trajectories of pre-administration samples but had a different extension on LRP1B mutation. h Repeated evolutionary trajectories that disappeared and were reborn after cetuximab treatment. GL stands for germline. Arrows indicate transitions. The number of times an alteration was clonal or subclonal in the cetuximab acquired resistant samples