Figure 1.
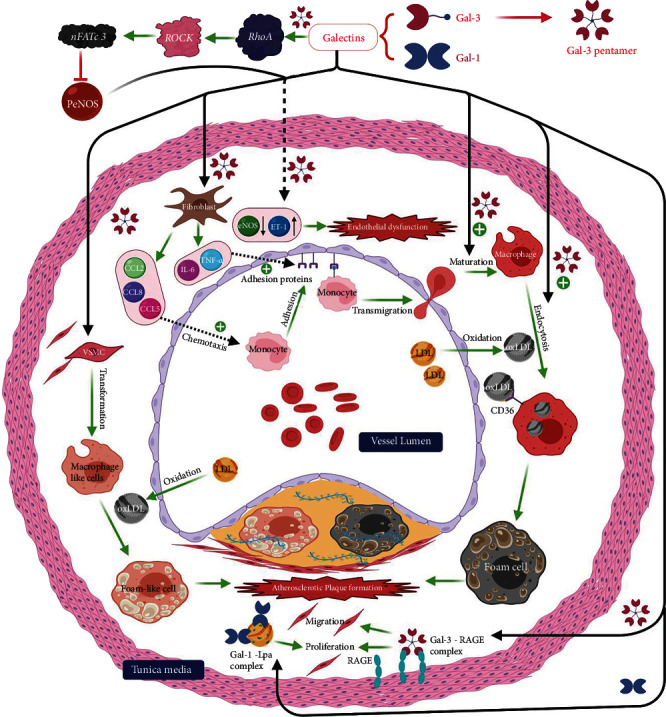
Demonstrates mechanisms and different pathways by which galectins can participate in the pathological process of atheromatous plaque formation as well as the induction of endothelial injury within blood vessels. RhoA: Ras homolog family member A; ROCK: Rho-associated protein kinase; nFATc3: nuclear factor of activated T-cells cytoplasmic 3; LDL: low-density lipoprotein; PeNOS: phospho-endothelial nitric oxide synthase; ET-1: endothelin 1; IL-6: interleukin 6; CD36: cluster of differentiation 36; VSMC: vascular smooth muscle cells; ox-LDL: oxidized LDL; RAGE: receptor for advanced glycation end products; TNF: tumor necrosis factor; CCL 2/5/8: inflammatory chemokine ligands. This figure was created via BioRender (http://www.BioRender.com).
