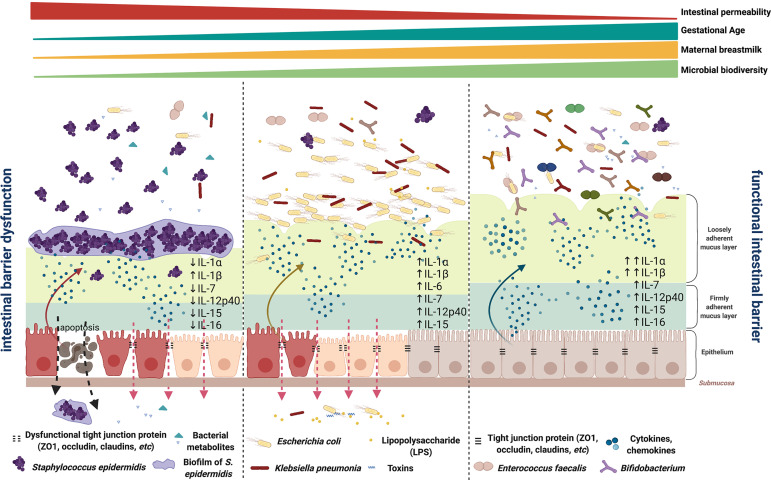
Figure 5.
Illustration of the intestinal barrier maturation in early preterm neonates with different microbiota types and cytokine profiles. An immature, compromised gut barrier may render the mucosa susceptible to invasion by opportunistic pathogens in the gut lumen. IP was linked with a microbial community dominated by a single species S. epidermidis, K. pneumoniae, or E. coli, with less defined cytokine profiles among individuals. A functional intestinal barrier was associated with neonates with later GA; higher BW; greater microbial community biodiversity that encompasses a wide array of anaerobic and facultative microorganisms not dominated by S. epidermidis, K. pneumoniae, or E. coli; and a trend of increased levels of IL-1α/β, IL-7, IL-12p40, IL-15, and IL-16. Schematic representation illustrates the distal intestine (not drawn to scale). Created with BioRender.com.