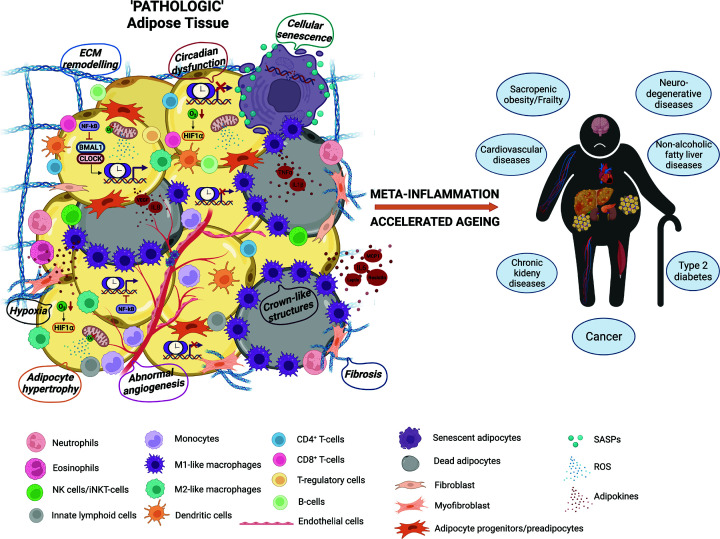
Figure 1. Pathologic reprogramming of WAT as the major culprit of obesity-associated diseases.
As a highly plastic endocrine organ, the AT undergoes extensive remodelling which involves hyperplasia/hypertrophy, fibrosis, angiogenesis and hypoxic response, chronic inflammation, cellular senescence and clock dysfunction. These abnormalities intertwine and escalate meta-inflammation and premature ageing, which ultimately manifest as obesity-related morbidities.