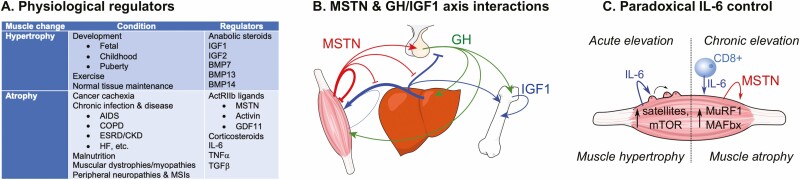
Figure 2.
Anabolic and catabolic regulation of muscle. (A) Parsing of general physiological and pathological conditions as well as the primary factors that differentially regulate skeletal muscle hypertrophy and atrophy (BMP, bone morphogenic protein; COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder; ESRD/CKD, end-stage renal disease/chronic kidney disease; GDF, growth/differentiation factor; HF, heart failure; MSTN, myostatin; MSI, musculoskeletal injury). (B) Model for MSTN interactions with the GH/IGF1 axis. Arrows represent stimulation, blocked lines inhibition. Arrow/line thickness is relative to influence. (C) Model for the paradoxical actions of IL-6 on skeletal muscle satellite cells and hypertrophy as well as on muscle protein degradation and atrophy. Colored arrows correspond to labeled factor, black arrows indicate increase (CD8+, cluster of differentiation 8 positive T-helper immune cell; MuRF1, muscle RING finger 1 [Trim63]; MAFbx, muscle atrophy F-Box [Atrogin-1]).