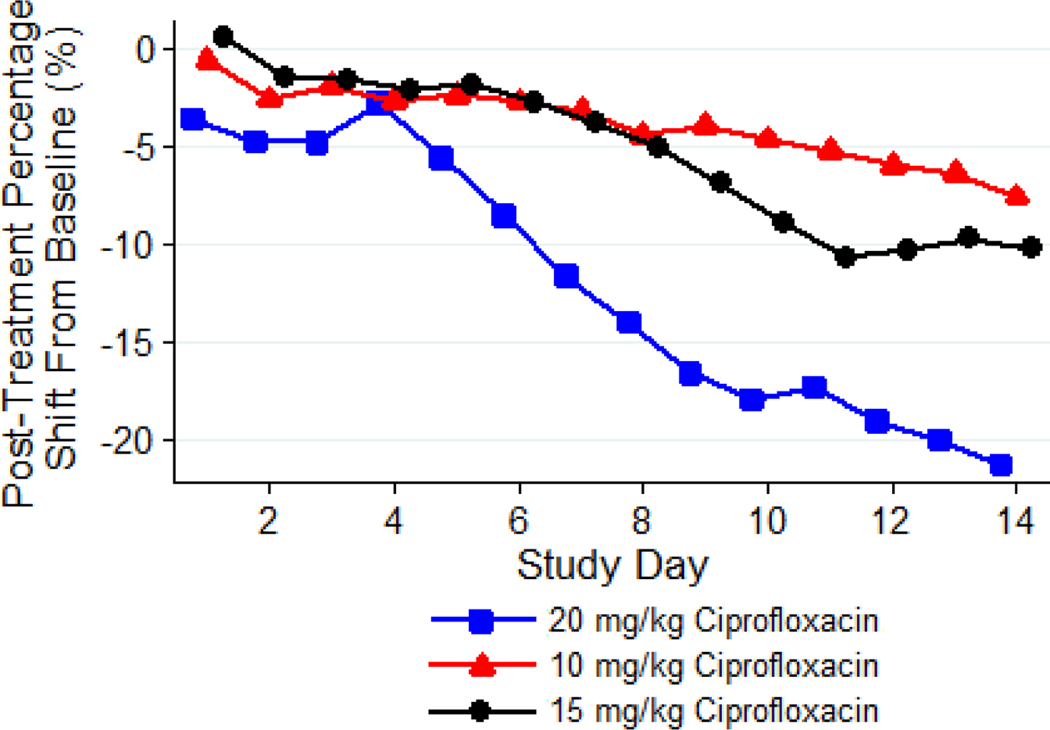
Figure 1: Mean Post-treatment Percentage Shift in Body Weights from Baseline over Time, by Group.
Guinea pigs (n = 8 per group) were treated with 10, 15, or 20 mg/kg of ciprofloxacin administered via IP injection TID for 14 days. The body weights were recorded daily. Based on the analysis of the weight loss, the 10 mg/kg dose of ciprofloxacin was well tolerated by guinea pigs, while tolerability was low and moderate at the 20 and 15 mg/kg. The decrease in body weight, compared to baseline, in the group administered 20 mg/kg of ciprofloxacin was significantly greater than in groups receiving lower dose levels of the antimicrobial (P < 0.05).