Fig. 1.
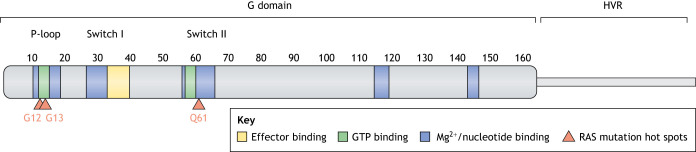
RAS structure and functional domains. The 164 N-terminal residues constitute the G domain, which is involved in GTP binding, effector interactions and Mg2+/nucleotide binding. Its Switch I and Switch II regions (aa 30-38 and 60-67, respectively) mediate protein interactions, and the P-loop region (aa 1-17) binds phosphate groups. The C-terminal end corresponds to the hypervariable region (HVR) of RAS, containing sequences that interact with the membrane. Indicated are amino acid positions G12, G13 and Q61 that are frequently mutated in cancer (G12D, G12V, G12C, G13D and Q61R), and account for 70% of all RAS mutants in patients (Prior et al., 2020).