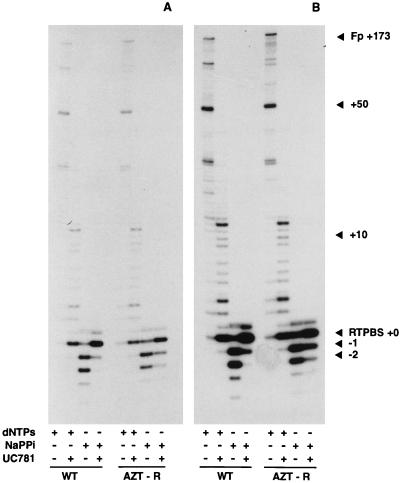
FIG. 2.
Inhibition of HIV-1 RT-catalyzed pyrophosphorolysis by UC781. All reaction mixtures contained 65 nM pHIV-PBS RNA and 5′-[32P]prPBS T-P (prepared as described in Materials and Methods) and 26 nM p51-p66 recombinant wt or AZT-resistant RT. Other components of the individual reaction mixtures are indicated by a plus sign. The final concentrations of these components were dNTPs (dATP, dCTP, dGTP, and TTP at 50 μM each), sodium PPi (NaPPi; 1 mM), and UC781 (1 μM). RT DNA synthesis reactions are those containing dNTPs but no sodium PPi. Pyrophosphorolysis reactions are those containing sodium PPi but no dNTPs. The extent of inhibition of these reactions is readily discerned by the intensity of the starting 18-nt [32P]prPBS primer (denoted as RTPBS+0). (A and B) Two different exposures of the same gel provided to facilitate comparison of the different reactions. The exposure for panel A emphasizes pyrophosphorolytic products, while that for panel B emphasizes the forward reaction DNA polymerization products. WT, reactions catalyzed by recombinant wild-type RT; AZT-R, reactions catalyzed by recombinant RT with the D67N, K70R, T215F, and K219Q mutations; Fp, full-length DNA product (primer extended by 173 nt).