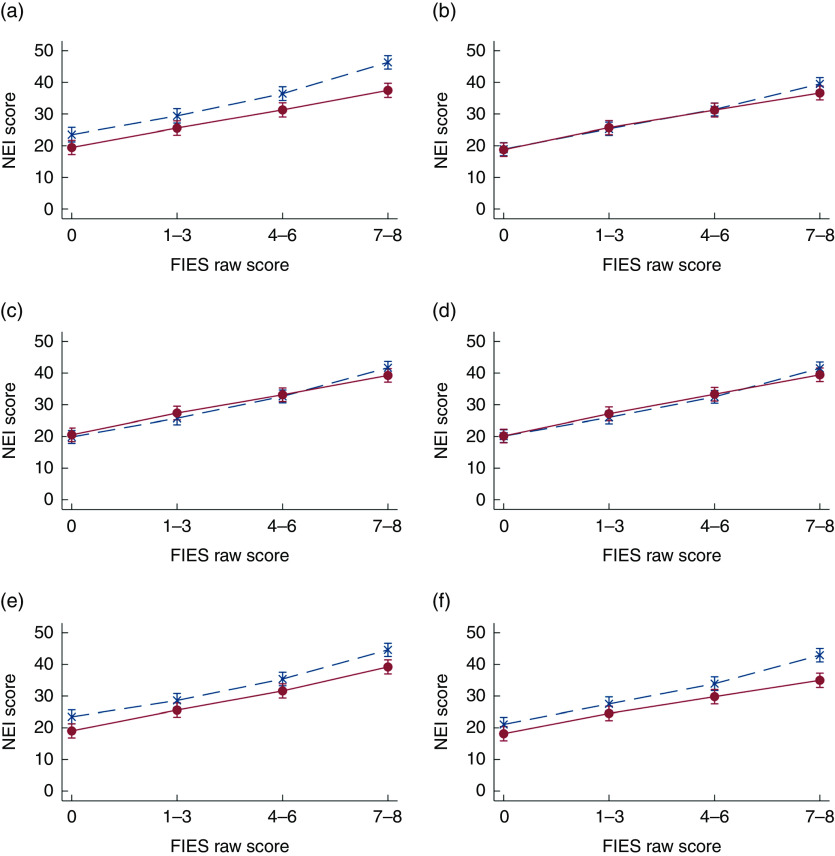
Fig. 1.
The marginal effect of food insecurity and types of social support (SS;  , no support;
, no support;  , yes support) on mental well-being assessed by Negative Experience Index (NEI) score (mean values with their standard errors represented by vertical bars) in sub-Saharan Africa, 2014–2016: (a) perceived SS; (b) foreign perceived SS; (c) received SS; (d) given SS; (e) integrative SS; (f) emotional SS. The relationship is adjusted for respondent’s age, sex, number of children under 15 years, number of adults over 15 years, education, employment status, place of residence, country-specific income quintiles and survey month. Food insecurity was measured using the Food Insecurity Experience Scale (FIES; raw scores represent four levels of food insecurity severity, with 7–8 being the most severe)
, yes support) on mental well-being assessed by Negative Experience Index (NEI) score (mean values with their standard errors represented by vertical bars) in sub-Saharan Africa, 2014–2016: (a) perceived SS; (b) foreign perceived SS; (c) received SS; (d) given SS; (e) integrative SS; (f) emotional SS. The relationship is adjusted for respondent’s age, sex, number of children under 15 years, number of adults over 15 years, education, employment status, place of residence, country-specific income quintiles and survey month. Food insecurity was measured using the Food Insecurity Experience Scale (FIES; raw scores represent four levels of food insecurity severity, with 7–8 being the most severe)